Heterologous expression of glucose oxidase in the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus
- PMID: 20092622
- PMCID: PMC2817671
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-9-4
Heterologous expression of glucose oxidase in the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus
Abstract
Background: In spite of its advantageous physiological properties for bioprocess applications, the use of the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus as a host for heterologous protein production has been very limited, in constrast to its close relative Kluyveromyces lactis. In the present work, the model protein glucose oxidase (GOX) from Aspergillus niger was cloned into K. marxianus CBS 6556 and into K. lactis CBS 2359 using three different expression systems. We aimed at verifying how each expression system would affect protein expression, secretion/localization, post-translational modification, and biochemical properties.
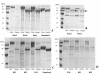
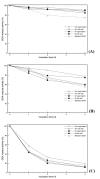
Results: The highest GOX expression levels (1552 units of secreted protein per gram dry cell weight) were achieved using an episomal system, in which the INU1 promoter and terminator were used to drive heterologous gene expression, together with the INU1 prepro sequence, which was employed to drive secretion of the enzyme. In all cases, GOX was mainly secreted, remaining either in the periplasmic space or in the culture supernatant. Whereas the use of genetic elements from Saccharomyces cerevisiae to drive heterologous protein expression led to higher expression levels in K. lactis than in K. marxianus, the use of INU1 genetic elements clearly led to the opposite result. The biochemical characterization of GOX confirmed the correct expression of the protein and showed that K. marxianus has a tendency to hyperglycosylate the protein, in a similar way as already observed for other yeasts, although this tendency seems to be smaller than the one of e.g. K. lactis and S. cerevisiae. Hyperglycosylation of GOX does not seem to affect its affinity for the substrate, nor its activity.
Conclusions: Taken together, our results indicate that K. marxianus is indeed a good host for the expression of heterologous proteins, not only for its physiological properties, but also because it correctly secretes and folds these proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Kiers J, Zeeman AM, Luttik M, Thiele C, Castrillo JI, Steensma HY, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT. Regulation of alcoholic fermentation in batch and chemostat cultures of Kluyveromyces lactis CBS 2359. Yeast. 1998;14(5):459–469. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(19980330)14:5<459::AID-YEA248>3.0.CO;2-O. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

