A comparative study of prenatal development in Miniopterus schreibersii fuliginosus, Hipposideros armiger and H. pratti
- PMID: 20092640
- PMCID: PMC2824742
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-10-10
A comparative study of prenatal development in Miniopterus schreibersii fuliginosus, Hipposideros armiger and H. pratti
Abstract
Background: Bats comprise the second largest order of mammals. However, there are far fewer morphological studies of post-implantation embryonic development than early embryonic development in bats.
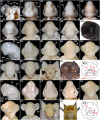
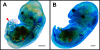
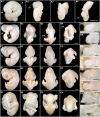
Results: We studied three species of bats (Miniopterus schreibersii fuliginosus, Hipposideros armiger and H. pratti), representing the two suborders Yangochiroptera and Yinpterochiroptera. Using an established embryonic staging system, we identified the embryonic stages for M. schreibersii fuliginosus, H. armiger and H. pratti and described the morphological changes in each species, including the development of the complex and distinctive nose-leaves in H. armiger and H. pratti. Finally, we compared embryonic and fetal morphology of the three species in the present study with five other species for which information is available.
Conclusion: As a whole, the organogenetic sequence of bat embryos is uniform and the embryos appear homoplastic before Stage 16. Morphological differentiation between species occurs mainly after embryonic Stage 16. Our study provides three new bat species for interspecific comparison of post-implantation embryonic development within the order Chiroptera and detailed data on the development of nose-leaves for bats in the superfamily Rhinolophoidea.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Call production and wingbeat coupling is flexible and species-specific in echolocating bats.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2025 May;1547(1):105-115. doi: 10.1111/nyas.15325. Epub 2025 Mar 30. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2025. PMID: 40159238
-
Ultrastructural development of chorioallantoic placenta in the Indian Miniopterus bat, Miniopterus schreibersii fuliginosus (Hodgson).Acta Anat (Basel). 1992;145(3):248-64. doi: 10.1159/000147374. Acta Anat (Basel). 1992. PMID: 1466238
-
Phylogenomic analyses of bat subordinal relationships based on transcriptome data.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 13;6:27726. doi: 10.1038/srep27726. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27291671 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrastructural observations of delayed implantation in the Japanese long-fingered bat, Miniopterus schreibersii fuliginosus.J Reprod Fertil. 1983 Sep;69(1):187-93. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0690187. J Reprod Fertil. 1983. PMID: 6887134
-
Natural epigenetic variation in bats and its role in evolution.J Exp Biol. 2015 Jan 1;218(Pt 1):100-6. doi: 10.1242/jeb.107243. J Exp Biol. 2015. PMID: 25568456 Review.
Cited by
-
Unique expression patterns of multiple key genes associated with the evolution of mammalian flight.Proc Biol Sci. 2014 Apr 2;281(1783):20133133. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.3133. Print 2014 May 22. Proc Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24695426 Free PMC article.
-
Differential cellular proliferation underlies heterochronic generation of cranial diversity in phyllostomid bats.Evodevo. 2020 Jun 2;11:11. doi: 10.1186/s13227-020-00156-9. eCollection 2020. Evodevo. 2020. PMID: 32514331 Free PMC article.
-
The Long Journey of Pontine Nuclei Neurons: From Rhombic Lip to Cortico-Ponto-Cerebellar Circuitry.Front Neural Circuits. 2017 May 17;11:33. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2017.00033. eCollection 2017. Front Neural Circuits. 2017. PMID: 28567005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the formation and diversification of a novel chiropteran wing membrane from embryonic development.BMC Biol. 2023 May 4;21(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12915-023-01598-y. BMC Biol. 2023. PMID: 37143038 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Hipposideros pratti.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2024 Jul 23;9(7):902-906. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2024.2381806. eCollection 2024. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2024. PMID: 39055531 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson DE, Reeder DM. Mammal species of the world: a taxonomic and geographic reference. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press; 2005.
-
- Crichton EG, Krutzsch PH. Reproductive biology of bats. London Academic Press; 2000.
-
- Hockman D, Mason MK, Jacobs DS, Illing N. The Role of Early Development in Mammalian Limb Diversification: A Descriptive Comparison of Early Limb Development Between the Natal Long-Fingered Bat (Miniopterus natalensis) and the Mouse (Mus musculus) Dev Dyn. 2009;238(4):965–979. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21896. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cretekos CJ, Weatherbee SD, Chen CH, Badwaik NK, Niswander L, Behringer RR, Rasweiler JJ IV. Embryonic staging system for the short-tailed fruit bat, Carollia perspicillata, a model organism for the mammalian order Chiroptera, based upon timed pregnancies in captive-bred animals. Dev Dyn. 2005;233:721–738. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20400. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

