Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of modafinil for the treatment of methamphetamine dependence
- PMID: 20092966
- PMCID: PMC2875545
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.11.023
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of modafinil for the treatment of methamphetamine dependence
Abstract
Objective: To compare modafinil to placebo for reducing methamphetamine (MA) use, improving retention, and reducing depressive symptoms and MA cravings. Rates of adverse events and cigarette smoking with modafinil versus placebo were also compared.
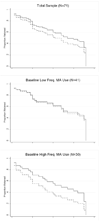
Methods: Following a 2-week, non-medication lead-in period, 71 treatment-seeking MA-dependent participants were randomly assigned to modafinil (400mg once daily; N=34) or placebo (once daily; N=37) for 12 weeks under double-blind conditions. Participants attended clinic thrice-weekly to provide urine samples analyzed for MA-metabolite, to complete research assessments, and to receive contingency management and weekly cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) sessions.
Results: There were no statistically significant effects for modafinil on MA use, retention, depressive symptoms, or MA cravings in pre-planned analyses. Outcomes for retention and MA use favored modafinil in a post hoc analysis among participants with low CBT attendance and among participants with baseline high-frequency of MA use (MA use on >18 of past 30 days), but did not reach statistical significance in these small subgroups. Modafinil was safe and well tolerated and did not increase cigarette smoking.
Conclusions: Modafinil was no more effective than placebo at 400mg daily in a general sample of MA users. A post hoc analysis showing a trend favoring modafinil among subgroups with baseline high-frequency MA use and low CBT attendance suggests that further evaluation of modafinil in MA users is warranted.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Anton RF, O'Malley SS, Ciraulo DA, Cisler RA, Couper D, Donovan DM, Gastfriend DR, Hosking JD, Johnson BA, LoCastro JS, Longabaugh R, Mason BJ, Mattson ME, Miller WR, Pettinati HM, Randall CL, Swift R, Weiss RD, Williams LD, Zweben A. Combined pharmacotherapies and behavioral interventions for alcohol dependence: the COMBINE study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295:2003–2017. - PubMed
-
- Batki S, Moon J, Delucchi K, Hersh D, Bradley M, Aguillon-Doms C, Mendelson J, Jones R, Panganiban T, Everhart T, Mengis M, Smolar S, Helmke H, Jacob P., III Amlodipine treatment of methamphetamine dependence, a controlled outpatient trial: preliminary analysis. The 63rd Annual Scientific Meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence; Scottsdale, AZ. 2001.
-
- Batki SL, Moon J, Bradley M, Hersh D, Smolar S, Mengis M, Delucchi K, Sexe D, Bennett S, Lefkowitz E, Chu W, Morello L, Jacob P, III, Jones RT. Fluoxetine in methamphetamine dependence-a controlled trial: preliminary analysis. The 61st Annual Scientific Meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence, Acapulco; Mexico. 1999.
-
- Bodenmann S, Xu S, Luhmann UFO, Arand M, Berger W, Jung HH, Landolt HP. Pharmacogenetics of Modafinil After Sleep Loss: Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Genotype Modulates Waking Functions But Not Recovery Sleep. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009;85:296–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

