Remodeling of cardiac fibroblasts following myocardial infarction results in increased gap junction intercellular communication
- PMID: 20093048
- PMCID: PMC2891425
- DOI: 10.1016/j.carpath.2009.12.002
Remodeling of cardiac fibroblasts following myocardial infarction results in increased gap junction intercellular communication
Abstract
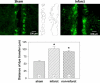
Background: We have recently shown that native murine ventricular fibroblasts express both connexin43 (Cx43) and Cx45, and that the level of Cx43 expression influences intercellular coupling and cell proliferation. Relatively little is known, however, about how myocardial infarction (MI) influences expression of Cx43, or how altered Cx43 expression may affect fibroblast function post-MI. Fibroblasts are critical for infarct healing and post-infarct ventricular remodeling. They can couple electrically with cardiac myocytes and influence myocardial activation patterns. Thus, Cx43 remodeling and the level of intercellular communication in fibroblasts expressed in the infarcted heart were the subject of the present investigation.
Methods: Fibroblasts were isolated from both infarct scar and remote, noninfarcted regions of murine hearts 6 d after coronary ligation. Expression levels of Cx43, α-smooth muscle actin and N-cadherin were quantified by immunoblotting. Gap junctional intercellular communication was quantified by Lucifer yellow dye transfer.
Results and conclusions: Fibroblasts isolated from infarcted hearts exhibited marked up-regulation of Cx43 protein expression and enhanced intercellular coupling. Exogenous administration of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) to fibroblast cultures from normal, non-operated hearts produced comparable up-regulation of Cx43, suggesting that increased intercellular communication between fibroblasts in infarct and peri-infarct regions may be secondary to activation of a TGF-β pathway. Unlike cardiac myocytes that down-regulate Cx43, presumably to limit intercellular transmission of biochemical mediators of ischemic injury, fibroblasts may up-regulate Cx43 to maintain electrical and metabolic coupling at a time when intercellular communication is compromised.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Reduced expression of Cx43 attenuates ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction via impaired TGF-beta signaling.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):H477-87. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00806.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19966054 Free PMC article.
-
Spatially and temporally distinct expression of fibroblast connexins after sheep ventricular infarction.Cardiovasc Res. 2004 May 1;62(2):415-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.01.027. Cardiovasc Res. 2004. PMID: 15094361
-
Connexin43 expression levels influence intercellular coupling and cell proliferation of native murine cardiac fibroblasts.Cell Commun Adhes. 2008 Sep;15(3):289-303. doi: 10.1080/15419060802198736. Cell Commun Adhes. 2008. PMID: 18923946 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical consequences of cardiac myocyte: fibroblast coupling.Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Jun;43(3):513-8. doi: 10.1042/BST20150035. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015. PMID: 26009200 Review.
-
Adrenergic control of cardiac gap junction function and expression.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011 Apr;383(4):331-46. doi: 10.1007/s00210-011-0603-4. Epub 2011 Feb 12. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21318337 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of connexin 43 by interleukin 1β in adult rat cardiac fibroblasts and effects in an adult rat cardiac myocyte: fibroblast co-culture model.Heliyon. 2019 Dec 30;6(1):e03031. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e03031. eCollection 2020 Jan. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31909243 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic value of circulating microRNAs in heart failure.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Mar;17(3):1985-2003. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7177. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30783473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Light Wand to Untangle the Myocardial Cell Network.Methods Protoc. 2019 May 3;2(2):34. doi: 10.3390/mps2020034. Methods Protoc. 2019. PMID: 31164614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Cardiac Fibroblast Number and Activation State Modulate Electromechanical Function of hiPSC-Cardiomyocytes in Engineered Myocardium.Stem Cells Int. 2020 Jul 16;2020:9363809. doi: 10.1155/2020/9363809. eCollection 2020. Stem Cells Int. 2020. PMID: 32724316 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast KATP currents modulate myocyte electrophysiology in infarcted hearts.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 May;304(9):H1231-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00878.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23436329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldsmith EC, Hoffman A, Morales MO, Potts JD, Price RL, McFadden A, Rice M, Borg TK. Organization of fibroblasts in the heart. Dev Dyn. 2004;230:787–794. - PubMed
-
- Camelliti P, Borg TK, Kohl P. Structural and functional characterisation of cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;65:40–51. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee I, Yekkala K, Borg TK, Baudino TA. Dynamic interactions between myocytes, fibroblasts, and extracellular matrix. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2006;1080:76–84. - PubMed
-
- Lijnen PJ, Petrov VV, Fagard RH. Induction of cardiac fibrosis by transforming growth factor-β1. Mol Genet Metab. 2000;71:418–435. - PubMed
-
- Manabe I, Shindo T, Nagai R. Gene expression in fibroblasts and fibrosis: involvement in cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res. 2002;91:1103–1113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

