Myricetin suppresses UVB-induced wrinkle formation and MMP-9 expression by inhibiting Raf
- PMID: 20093107
- PMCID: PMC2864126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.01.004
Myricetin suppresses UVB-induced wrinkle formation and MMP-9 expression by inhibiting Raf
Abstract
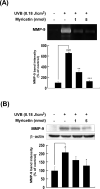
Chronic exposure to solar ultraviolet (UV) light causes skin photoaging. Many studies have shown that naturally occurring phytochemicals have anti-photoaging effects, but their direct target molecule(s) and mechanism(s) remain unclear. We found that myricetin, a major flavonoid in berries and red wine, inhibited wrinkle formation in mouse skin induced by chronic UVB irradiation (0.18J/cm(2), 3 days/week for 15 weeks). Myricetin treatment reduced UVB-induced epidermal thickening of mouse skin and also suppressed UVB-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) protein expression and enzyme activity. Myricetin appeared to exert its anti-aging effects by suppressing UVB-induced Raf kinase activity and subsequent attenuation of UVB-induced phosphorylation of MEK and ERK in mouse skin. In vitro and in vivo pull-down assays revealed that myricetin bound with Raf in an ATP-noncompetitive manner. Overall, these results indicate that myricetin exerts potent anti-photoaging activity by regulating MMP-9 expression through the suppression of Raf kinase activity.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Sams WM, Jr., Smith JG., Jr. The histochemistry of chronically sun-damaged skin. An investigation of mucopolysaccharides and basophilia in actinically damaged skin using alcian blue, mowry's, and Hicks-Matthaei stains, methylation, and saponification. J Invest Dermatol. 1961;37:447–53. - PubMed
-
- Smith JG, Jr., Davidson EA, Sams WM, Jr., Clark RD. Alterations in human dermal connective tissue with age and chronic sun damage. J Invest Dermatol. 1962;39:347–50. - PubMed
-
- Gilchrest BA. A review of skin ageing and its medical therapy. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:867–75. - PubMed
-
- Grewe M, Trefzer U, Ballhorn A, Gyufko K, Henninger H, Krutmann J. Analysis of the mechanism of ultraviolet (UV) B radiation-induced prostaglandin E2 synthesis by human epidermoid carcinoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101:528–31. - PubMed
-
- Chung JH, Seo JY, Choi HR, Lee MK, Youn CS, Rhie G, et al. Modulation of skin collagen metabolism in aged and photoaged human skin in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;117:1218–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

