Physical interaction of Jab1 with human serotonin 6 G-protein-coupled receptor and their possible roles in cell survival
- PMID: 20093369
- PMCID: PMC2843165
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.068759
Physical interaction of Jab1 with human serotonin 6 G-protein-coupled receptor and their possible roles in cell survival
Abstract
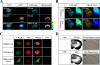
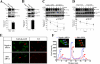
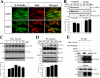
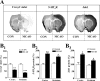
The 5-HT(6) receptor (5-HT(6)R) is one of the most recently cloned serotonin receptors, and it plays important roles in Alzheimer disease, depression, and learning and memory disorders. However, unlike the other serotonin receptors, the cellular mechanisms of 5-HT(6)R are poorly elucidated relative to its significance in human brain diseases. Here, using a yeast two-hybrid assay, we found that the human 5-HT(6)R interacts with Jun activation domain-binding protein-1 (Jab1). We also confirmed a physical interaction between 5-HT(6)R and Jab1 using glutathione S-transferase pulldown, fluorescence resonance energy transfer, co-immunoprecipitation, and immunocyto(histo)chemistry assays. The manipulation of Jab1 expression using Jab1 small interference RNA decreased 5-HT(6)R-mediated activity and cell membrane expression of 5-HT(6)R, whereas overexpression of Jab1 produced no significant effect. In addition, we demonstrated that the activation of 5-HT(6)R induced the translocation of Jab1 into the nucleus and increased c-Jun phosphorylation and the interaction between Jab1 and c-Jun. Furthermore, we found that 5-HT(6)R and Jab1 were up-regulated in middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced focal cerebral ischemic rats and in cultured cells exposed to hypoxic insults, suggesting possible protective roles for 5-HT(6)R and Jab1. These findings suggest that Jab1 provides a novel signal transduction pathway for 5-HT(6)R and may play an important role in 5-HT(6)R-mediated behavior changes in the brain.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Jab1, a novel protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR-2)-interacting protein, is involved in PAR-2-induced activation of activator protein-1.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 24;281(12):7927-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510784200. Epub 2006 Jan 12. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16410250
-
The novel cellular mechanism of human 5-HT6 receptor through an interaction with Fyn.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 23;282(8):5496-505. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M606215200. Epub 2006 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17189269
-
Characterization of a unique motif in LIM mineralization protein-1 that interacts with jun activation-domain-binding protein 1.Mol Cell Biochem. 2014 Jan;385(1-2):145-57. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1823-3. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24078030 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential of JAB1 in neurological development and disorders.Mol Med. 2023 Jun 26;29(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00675-w. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37365502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic role of c-Jun activation domain-binding protein-1 in cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Mar;25(6):2750-2763. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16334. Epub 2021 Feb 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33550701 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential Genes and Mechanisms Linking Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Depression: A Bioinformatics-Based Study.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Apr 7;14:1213-1226. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S302916. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 33854363 Free PMC article.
-
Excess of serotonin affects neocortical pyramidal neuron migration.Transl Psychiatry. 2011 Oct 11;1(10):e47. doi: 10.1038/tp.2011.49. Transl Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 22833193 Free PMC article.
-
JAB1/CSN5: a new player in cell cycle control and cancer.Cell Div. 2010 Oct 18;5:26. doi: 10.1186/1747-1028-5-26. Cell Div. 2010. PMID: 20955608 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in Investigational Agents Targeting Serotonin-6 Receptors for the Treatment of Brain Disorders.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 7;13(2):309. doi: 10.3390/biom13020309. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin 5-HT6 Receptor Antagonists in Alzheimer's Disease: Therapeutic Rationale and Current Development Status.CNS Drugs. 2017 Jan;31(1):19-32. doi: 10.1007/s40263-016-0399-3. CNS Drugs. 2017. PMID: 27914038 Review.
References
-
- Barnes N. M., Sharp T. (1999) Neuropharmacology 38, 1083–1152 - PubMed
-
- Kohen R., Metcalf M. A., Khan N., Druck T., Huebner K., Lachowicz J. E., Meltzer H. Y., Sibley D. R., Roth B. L., Hamblin M. W. (1996) J. Neurochem. 66, 47–56 - PubMed
-
- Ward R. P., Hamblin M. W., Lachowicz J. E., Hoffman B. J., Sibley D. R., Dorsa D. M. (1995) Neuroscience 64, 1105–1111 - PubMed
-
- Roth B. L., Craigo S. C., Choudhary M. S., Uluer A., Monsma F. J., Jr., Shen Y., Meltzer H. Y., Sibley D. R. (1994) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 268, 1403–1410 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

