Evolution of MRSA during hospital transmission and intercontinental spread
- PMID: 20093474
- PMCID: PMC2821690
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1182395
Evolution of MRSA during hospital transmission and intercontinental spread
Abstract
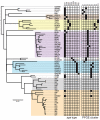
Current methods for differentiating isolates of predominant lineages of pathogenic bacteria often do not provide sufficient resolution to define precise relationships. Here, we describe a high-throughput genomics approach that provides a high-resolution view of the epidemiology and microevolution of a dominant strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). This approach reveals the global geographic structure within the lineage, its intercontinental transmission through four decades, and the potential to trace person-to-person transmission within a hospital environment. The ability to interrogate and resolve bacterial populations is applicable to a range of infectious diseases, as well as microbial ecology.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

