Lack of a major role of Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine leukocidin in lower respiratory tract infection in nonhuman primates
- PMID: 20093487
- PMCID: PMC2832154
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090960
Lack of a major role of Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine leukocidin in lower respiratory tract infection in nonhuman primates
Abstract
Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) is a two-component cytolytic toxin epidemiologically linked to community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) infections, including serious invasive infections caused by the epidemic clone referred to as strain USA300. Although PVL has long been known to be a S. aureus virulence molecule in vitro, the relative contribution of this leukotoxin to invasive CA-MRSA infections such as pneumonia remains controversial. We developed a nonhuman primate model of CA-MRSA pneumonia and used it to test the hypothesis that PVL contributes to lower respiratory tract infections caused by S. aureus strain USA300. The lower respiratory tract disease observed in this monkey model mimicked the clinical and pathological features of early mild to moderate S. aureus pneumonia in humans, including fine-structure histopathology. In this experiment using a large sample of monkeys and multiple time points of examination, no involvement of PVL in virulence could be detected. Compared with the wild-type parental USA300 strain, the isogenic PVL deletion-mutant strain caused equivalent lower respiratory tract pathology. We conclude that PVL does not contribute to lower respiratory tract infection in this nonhuman primate model of human CA-MRSA pneumonia.
Figures
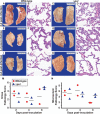
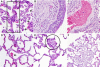
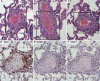
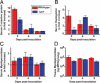
Similar articles
-
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes mediate Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine leukocidin-induced lung inflammation and injury.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Mar 23;107(12):5587-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912403107. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20231457 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus corneal infections: effect of the Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) and antibody to PVL on virulence and pathology.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Jul 1;54(7):4430-8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-11701. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23737477 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription of inflammatory genes in the lung after infection with community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a role for panton-valentine leukocidin?Infect Immun. 2009 May;77(5):2159-67. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00021-09. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19237525 Free PMC article.
-
Review on Panton Valentine leukocidin toxin carriage among Staphylococcus aureus.J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2013 Sep;11(25):305-12. J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2013. PMID: 24908537 Review.
-
The role of Panton-Valentine leukocidin in Staphylococcus aureus musculoskeletal infections in children.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012 May;31(5):514-8. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31824f18cb. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012. PMID: 22327874 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive Factors of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection in Elderly Patients with Community-Onset Pneumonia.Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2017 Apr;80(2):201-209. doi: 10.4046/trd.2017.80.2.201. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2017. PMID: 28416961 Free PMC article.
-
Community-acquired necrotizing pneumonia due to methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus secreting Panton-Valentine leukocidin: a review of case reports.Ann Intensive Care. 2011 Dec 22;1(1):52. doi: 10.1186/2110-5820-1-52. Ann Intensive Care. 2011. PMID: 22192614 Free PMC article.
-
Nonhuman primate species as models of human bacterial sepsis.Lab Anim (NY). 2019 Feb;48(2):57-65. doi: 10.1038/s41684-018-0217-2. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Lab Anim (NY). 2019. PMID: 30643274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virulence strategies of the dominant USA300 lineage of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA).FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012 Jun;65(1):5-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2012.00937.x. Epub 2012 Mar 5. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22309135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A naturally occurring single amino acid replacement in multiple gene regulator of group A Streptococcus significantly increases virulence.Am J Pathol. 2015 Feb;185(2):462-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.10.018. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Am J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25476528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klevens RM, Morrison MA, Nadle J, Petit S, Gersham K, Ray S, Harrison LH, Lynfield R, Dumyati G, Townes JM, Craig AS, Zell ER, Fosheim GE, McDougal LK, Carey RB, Fridkin SK. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298:1763–1771. - PubMed
-
- Moran GJ, Krishnadasan A, Gorwitz RJ, Fosheim GE, McDougal LK, Carey RB, Talan DA. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections among patients in the emergency department. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:666–674. - PubMed
-
- Noskin GA, Rubin RJ, Schentag JJ, Kluytmans J, Hedblom EC, Jacobson C, Smulders M, Gemmen E, Bharmal M. National trends in Staphylococcus aureus infection rates: impact on economic burden and mortality over a 6-year period (1998–2003) Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:1132–1140. - PubMed
-
- Klevens RM, Edwards JR, Tenover FC, McDonald LC, Horan T, Gaynes R. Changes in the epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in intensive care units in US hospitals, 1992–2003. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:389–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

