Incremental value of adenosine-induced stress myocardial perfusion imaging with dual-source CT at cardiac CT angiography
- PMID: 20093513
- PMCID: PMC2809927
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.09091014
Incremental value of adenosine-induced stress myocardial perfusion imaging with dual-source CT at cardiac CT angiography
Abstract
Purpose: First, to assess the feasibility of a protocol involving stress-induced perfusion evaluated at computed tomography (CT) combined with cardiac CT angiography in a single examination and second, to assess the incremental value of perfusion imaging over cardiac CT angiography in a dual-source technique for the detection of obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) in a high-risk population.
Materials and methods: Institutional review board approval and informed patient consent were obtained before patient enrollment in the study. The study was HIPAA compliant. Thirty-five patients at high risk for CAD were prospectively enrolled for evaluation of the feasibility of CT perfusion imaging. All patients underwent retrospectively electrocardiographically gated (helical) adenosine stress CT perfusion imaging followed by prospectively electrocardiographically gated (axial) rest myocardial CT perfusion imaging. Analysis was performed in three steps: (a)Coronary arterial stenoses were scored for severity and reader confidence at cardiac CT angiography, (b)myocardial perfusion defects were identified and scored for severity and reversibility at CT perfusion imaging, and (c)coronary stenosis severity was reclassified according to perfusion findings at combined cardiac CT angiography and CT perfusion imaging. The sensitivity, specificity, negative predictive value (NPV), and positive predictive value (PPV) of cardiac CT angiography before and after CT perfusion analysis were calculated.
Results: With use of a reference standard of greater than 50% stenosis at invasive angiography, all parameters of diagnostic accuracy increased after CT perfusion analysis: Sensitivity increased from 83% to 91%; specificity, from 71% to 91%; PPV, from 66% to 86%; and NPV, from 87% to 93%. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve increased significantly, from 0.77 to 0.90 (P < .005).
Conclusion: A combination protocol involving adenosine perfusion CT imaging and cardiac CT angiography in a dual-source technique is feasible, and CT perfusion adds incremental value to cardiac CT angiography in the detection of significant CAD.
(c) RSNA, 2010.
Figures

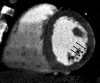





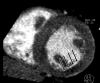

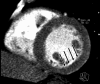

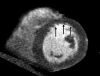

Comment in
-
Myocardial perfusion imaging with multidetector CT: beyond lumenography.Radiology. 2010 Feb;254(2):321-3. doi: 10.1148/radiol.09092106. Radiology. 2010. PMID: 20093505 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic performance of combined noninvasive anatomic and functional assessment with dual-source CT and adenosine-induced stress dual-energy CT for detection of significant coronary stenosis.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012 Mar;198(3):512-20. doi: 10.2214/AJR.11.7029. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012. PMID: 22357990
-
Adenosine-stress low-dose single-scan CT myocardial perfusion imaging using a 128-slice dual-source CT: a comparison with fractional flow reserve.Acta Radiol. 2013 May;54(4):389-95. doi: 10.1177/0284185113475440. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Acta Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23550182
-
CT myocardial perfusion and coronary CT angiography: Influence of coronary calcium on a stress-rest protocol.J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2016 May-Jun;10(3):215-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2016.01.013. Epub 2016 Jan 30. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2016. PMID: 26869367
-
Diagnostic Performance of Hybrid Cardiac Imaging Methods for Assessment of Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease Compared With Stand-Alone Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography: A Meta-Analysis.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Apr;11(4):589-599. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2017.05.020. Epub 2017 Aug 16. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018. PMID: 28823745 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of Non-Gated Chest Computed Tomography Scans in Predicting Acute Coronary Occlusion in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2022 Oct;47(10):101276. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2022.101276. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35667497 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenosine-stress dynamic myocardial perfusion imaging using 128-slice dual-source CT: optimization of the CT protocol to reduce the radiation dose.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Apr;29(4):875-84. doi: 10.1007/s10554-012-0138-x. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23076604
-
Current status of cardiac CT for the detection of myocardial ischemia.Herz. 2013 Jun;38(4):359-66. doi: 10.1007/s00059-013-3805-3. Herz. 2013. PMID: 23588608
-
CT perfusion: ready for prime time.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2011 Feb;13(1):57-66. doi: 10.1007/s11886-010-0152-3. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21080111 Review.
-
Myocardial blood flow quantification for evaluation of coronary artery disease by positron emission tomography, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, and computed tomography.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2014 May;16(5):483. doi: 10.1007/s11886-014-0483-6. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24718671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic performance of dual-energy CT stress myocardial perfusion imaging: direct comparison with cardiovascular MRI.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014 Dec;203(6):W605-13. doi: 10.2214/AJR.14.12644. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014. PMID: 25415725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achenbach S, Ropers U, Kuettner A, et al. Randomized comparison of 64-slice single- and dual-source computed tomography coronary angiography for the detection of coronary artery disease. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2008;1:177–186 - PubMed
-
- Budoff MJ, Dowe D, Jollis JG, et al. Diagnostic performance of 64-multidetector row coronary computed tomographic angiography for evaluation of coronary artery stenosis in individuals without known coronary artery disease: results from the prospective multicenter ACCURACY (Assessment by Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography of Individuals Undergoing Invasive Coronary Angiography) Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;52:1724–1732 - PubMed
-
- Husmann L, Schepis T, Scheffel H, et al. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of 64-slice computed tomography coronary angiography in patients with low, intermediate, and high cardiovascular risk. Acad Radiol 2008;15:452–461 - PubMed
-
- Johnson TR, Nikolaou K, Busch S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of dual-source computed tomography in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Invest Radiol 2007;42:684–691 - PubMed
-
- Meijboom WB, Meijs MF, Schuijf JD, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of 64-slice computed tomography coronary angiography: a prospective, multicenter, multivendor study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;52:2135–2144 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

