Targeting the cancer kinome through polypharmacology
- PMID: 20094047
- PMCID: PMC2880454
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc2787
Targeting the cancer kinome through polypharmacology
Abstract
Kinase inhibitors are the largest class of new cancer drugs. However, it is already apparent that most tumours can escape from the inhibition of any single kinase. If it is necessary to inhibit multiple kinases, how do we choose which ones? In this Opinion article, we discuss some of the strategies that are currently being used to identify new therapeutic combinations of kinase targets.
Figures


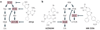

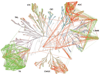
References
-
- Akritopoulou-Zanze I, Hajduk PJ. Kinase-targeted libraries: the design and synthesis of novel, potent, and selective kinase inhibitors. Drug Discov. Today. 2009;14:291–297. - PubMed
-
- Parsons DW, et al. Colorectal cancer: mutations in a signalling pathway. Nature. 2005;436:792. - PubMed
-
- Wood LD, et al. The genomic landscapes of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science. 2007;318:1108–1113. - PubMed
-
- Sjoblom T, et al. The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science. 2006;314:268–274. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;344:1031–1037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

