Myosin VI: an innovative motor that challenged the swinging lever arm hypothesis
- PMID: 20094053
- PMCID: PMC2859320
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm2833
Myosin VI: an innovative motor that challenged the swinging lever arm hypothesis
Abstract
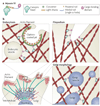
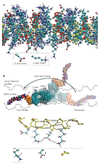
The swinging crossbridge hypothesis states that energy from ATP hydrolysis is transduced to mechanical movement of the myosin head while bound to actin. The light chain-binding region of myosin is thought to act as a lever arm that amplifies movements near the catalytic site. This model has been challenged by findings that myosin VI takes larger steps along actin filaments than early interpretations of its structure seem to allow. We now know that myosin VI does indeed operate by an unusual approximately 180 degrees lever arm swing and achieves its large step size using special structural features in its tail domain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
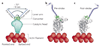




Similar articles
-
Processive steps in the reverse direction require uncoupling of the lead head lever arm of myosin VI.Mol Cell. 2012 Oct 12;48(1):75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.07.034. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22940248 Free PMC article.
-
Long single alpha-helical tail domains bridge the gap between structure and function of myosin VI.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Jun;15(6):591-7. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1429. Epub 2008 May 30. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18511944 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin VI undergoes a 180 degrees power stroke implying an uncoupling of the front lever arm.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Oct 27;106(43):18255-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900005106. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19828438 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin VI rewrites the rules for myosin motors.Cell. 2010 May 14;141(4):573-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.028. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20478251 Review.
-
Myosin VI: cellular functions and motor properties.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2004 Dec 29;359(1452):1931-44. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2004.1563. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15647169 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myosin motors at neuronal synapses: drivers of membrane transport and actin dynamics.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Apr;14(4):233-47. doi: 10.1038/nrn3445. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23481482 Review.
-
Multiple myosin motors interact with sodium/potassium-ATPase alpha 1 subunits.Mol Brain. 2018 Aug 7;11(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13041-018-0388-1. Mol Brain. 2018. PMID: 30086768 Free PMC article.
-
Parsing the roles of neck-linker docking and tethered head diffusion in the stepping dynamics of kinesin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Nov 14;114(46):E9838-E9845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1706014114. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29087307 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of ethanol analgesia quantitative trait loci and candidate genes in BXD recombinant inbred mouse lines.Addict Biol. 2025 Feb;30(2):e70013. doi: 10.1111/adb.70013. Addict Biol. 2025. PMID: 39996569 Free PMC article.
-
Detailed tuning of structure and intramolecular communication are dispensable for processive motion of myosin VI.Biophys J. 2011 Jan 19;100(2):430-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.11.045. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21244839 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Huxley HE. The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science. 1969;164:1356–1365. Proposes the swinging crossbridge hypothesis, which was later called the swinging lever arm hypothesis.
-
-
-
Menetrey J, et al. The structure of the myosin VI motor reveals the mechanism of directionality reversal. Nature. 2005;435:779–785. Presents the crystal structure of myosin VI in its post-stroke state, which reveals a redirection of the lever arm by the unique insert, first proposed here to be the source of the reverse directionality of this motor.
-
-
-
Menetrey J, Llinas P, Mukherjea M, Sweeney HL, Houdusse A. The structural basis for the large powerstroke of myosin VI. Cell. 2007;131:300–308. Presents the crystal structure of myosin VI in its pre-stroke state, and reveals an unexpected change in conformation of the converter that allows a 180° rotation of the myosin VI lever arm.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

