Tongue epithelial KT-1 cell-cycle arrest by TGF-beta associated with induction of p21(Cip1) and p15 (Ink4b)
- PMID: 20094776
- PMCID: PMC2825299
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-010-9251-7
Tongue epithelial KT-1 cell-cycle arrest by TGF-beta associated with induction of p21(Cip1) and p15 (Ink4b)
Abstract
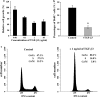
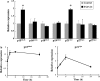
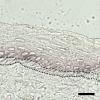
Tongue epithelium continuously turns over in adults. Our previous study showed that epidermal growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2 stimulated proliferation of KT-1 cells derived from tongue epithelium, suggesting that these signals serve as positive regulators for tongue epithelial proliferation. To investigate a negative regulation of tongue epithelial cell proliferation, we studied effects of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) on KT-1 cells. Proliferation assays showed that TGF-beta inhibited proliferation of KT-1 cells in a dose dependent manner. Cell-cycle analysis showed that TGF-beta induced G(0)/G(1) cell cycle arrest in KT-1 cells. We also examined expressions of Ink4 and Cip/Kip family mRNA by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. We found that TGF-beta induced p15(Ink4b) and p21(Cip1) mRNA expressions. These results strongly suggest that G(0)/G(1) cell cycle arrest is associated with increased p15(Ink4b) and p21(Cip1) expressions. Moreover, p21(Cip1) mRNA was localized in suprabasal cells of tongue epithelium, suggesting that p21(Cip1) play a role in cell-cycle exit along with tongue epithelial differentiation. Taken together, our results suggest that TGF-beta signaling serves as negative regulator of tongue epithelial cell proliferation, and may control tongue epithelial cell differentiation through modulating expression of p21(Cip1).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Decreased proliferation and cell cycle arrest in neoplastic rat pituitary cells is associated with transforming growth factor-beta1-induced expression of p15/INK4B.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001 May 15;176(1-2):29-37. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00477-4. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11369440
-
Transforming growth factor-beta induces senescence in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and inhibits tumor growth.Hepatology. 2010 Sep;52(3):966-74. doi: 10.1002/hep.23769. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20583212
-
The viral oncoprotein E1A blocks transforming growth factor beta-mediated induction of p21/WAF1/Cip1 and p15/INK4B.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Apr;17(4):2030-7. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.4.2030. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9121451 Free PMC article.
-
p21Cip1 and p27Kip1 act in synergy to alter the sensitivity of naive T cells to TGF-beta-mediated G1 arrest through modulation of IL-2 responsiveness.J Immunol. 2004 Sep 1;173(5):3093-102. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.3093. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15322169
-
Transforming growth factor-beta-mediated p15(INK4B) induction and growth inhibition in astrocytes is SMAD3-dependent and a pathway prominently altered in human glioma cell lines.J Biol Chem. 1999 Dec 3;274(49):35053-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.49.35053. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10574984
Cited by
-
The paradoxical role of transforming growth factor-β in controlling oral squamous cell carcinoma development.Cancer Biomark. 2024;40(3-4):241-250. doi: 10.3233/CBM-230354. Cancer Biomark. 2024. PMID: 39213051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular senescence mediates retinal ganglion cell survival regulation post-optic nerve crush injury.Cell Prolif. 2024 Dec;57(12):e13719. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13719. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 39021340 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of clonal cell lines of taste buds from a p53(-/-) mouse tongue.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011 Apr;47(4):333-40. doi: 10.1007/s11626-011-9398-3. Epub 2011 Mar 25. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011. PMID: 21437573
-
Stress as worsening of the signs and symptoms of the geographic tongue during the COVID-19 pandemic: a pilot study.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Dec 3;22(1):565. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02609-0. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 36463206 Free PMC article.
-
Immortalization and Characterization of Rat Lingual Keratinocytes in a High-Calcium and Feeder-Free Culture System Using ROCK Inhibitor Y-27632.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 24;22(13):6782. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136782. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34202585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheifetz S, Hernandez H, Laiho M, Ten Dijke P, Iwata KK, Massague J. Distinct transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) receptor subsets as determinants of cellular responsiveness to three TGF-beta isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:20533–20538. - PubMed
-
- Ding QM, Ko TC, Evers BM. Caco-2 intestinal cell differentiation is associated with G1 arrest and suppression of CDK2 and CDK4. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:C1193–C1200. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

