An integrated molecular dynamics (MD) and experimental study of higher order human telomeric quadruplexes
- PMID: 20095044
- PMCID: PMC3131549
- DOI: 10.1002/bip.21392
An integrated molecular dynamics (MD) and experimental study of higher order human telomeric quadruplexes
Abstract
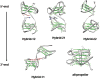
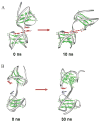
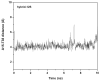
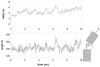
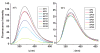
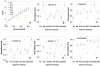
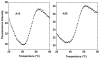
Structural knowledge of telomeric DNA is critical for understanding telomere biology and for the utilization of telomeric DNA as a therapeutic target. Very little is known about the structure of long human DNA sequences that may form more than one quadruplex unit. Here, we report a combination of molecular dynamics simulations and experimental biophysical studies to explore the structural and dynamic properties of the human telomeric sequence (TTAGGG)(8)TT that folds into two contiguous quadruplexes. Five higher order quadruplex models were built combining known single human telomeric quadruplex structures as unique building blocks. The biophysical properties of this sequence in K(+) solution were experimentally investigated by means of analytical ultracentrifugation and UV spectroscopy. Additionally, the environments of loop adenines were probed by fluorescence studies using systematic single-substitutions of 2-aminopurine for the adenine bases. The comparison of the experimentally determined properties with the corresponding quantities predicted from the models allowed us to test the validity of each of the structural models. One model emerged whose properties are most consistent with the predictions, and which therefore is the most probable structure in solution. This structure features contiguous quadruplex units in an alternating hybrid-1-hybrid-2 conformation with a highly ordered interface composed of loop residues from both quadruplexes.
(c) 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Not so crystal clear: the structure of the human telomere G-quadruplex in solution differs from that present in a crystal.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Aug 16;33(14):4649-59. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki782. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16106044 Free PMC article.
-
Human telomeric sequence forms a hybrid-type intramolecular G-quadruplex structure with mixed parallel/antiparallel strands in potassium solution.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 May 19;34(9):2723-35. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl348. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16714449 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the intramolecular human telomeric G-quadruplex in potassium solution: a novel adenine triple formation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(7):2440-50. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm009. Epub 2007 Mar 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17395643 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphism of human telomeric quadruplex structures.Biochimie. 2008 Aug;90(8):1172-83. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2008.02.026. Epub 2008 Mar 8. Biochimie. 2008. PMID: 18373984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Higher-order quadruplex structures.Top Curr Chem. 2013;330:23-46. doi: 10.1007/128_2012_350. Top Curr Chem. 2013. PMID: 22790417 Review.
Cited by
-
G-quadruplex structure and stability illuminated by 2-aminopurine phasor plots.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 May;40(9):4203-15. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1286. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22241767 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-RNA hybrid G-quadruplex tends to form near the 3' end of telomere overhang.Biophys J. 2022 Aug 2;121(15):2962-2980. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.06.026. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 35769005 Free PMC article.
-
Calculation of hydrodynamic properties for G-quadruplex nucleic acid structures from in silico bead models.Top Curr Chem. 2013;330:179-210. doi: 10.1007/128_2012_351. Top Curr Chem. 2013. PMID: 22886555 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and stability of higher-order human telomeric quadruplexes.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Dec 28;133(51):20951-61. doi: 10.1021/ja209192a. Epub 2011 Dec 1. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 22082001 Free PMC article.
-
Single molecule studies of physiologically relevant telomeric tails reveal POT1 mechanism for promoting G-quadruplex unfolding.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 4;286(9):7479-89. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.205641. Epub 2010 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21183684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blackburn EH. Nature. 1991;350:569–573. - PubMed
-
- Rhodes D, Giraldo R. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1995;5:311–322. - PubMed
-
- Bryan TM, Cech TR. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:318–324. - PubMed
-
- Harley CB, Futcher AB, Greider CW. Nature. 1990;345:458–460. - PubMed
-
- Allsopp RC, Harley CB. Exp Cell Res. 1995;219:130–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

