Swallowing problems and dementia in acute hospital settings: practical guidance for the management of dysphagia
- PMID: 20095295
- PMCID: PMC4952291
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmedicine.9-6-544
Swallowing problems and dementia in acute hospital settings: practical guidance for the management of dysphagia
Abstract
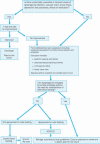
There is little evidence to support tube feeding in advanced dementia although it is still frequently used in acute hospital settings. Patients present with complex problems and are often unable to make decisions about their healthcare needs. Multidisciplinary teams may be challenged by the difficult ethical decisions they are required to make in the best interests of their patients. This paper guides decision making in the management of patients with dementia and dysphagia in the acute hospital setting. A structured approach to information gathering, assessment and management is outlined with practical application of recent published guidelines and research evidence, which ensures appropriate individualised care.
Figures
Comment in
-
Swallowing and dementia--practical solutions for a highly emotive problem?Clin Med (Lond). 2010 Jun;10(3):305-6. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.10-3-305a. Clin Med (Lond). 2010. PMID: 20731063 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Dementia: supporting people with dementia and their carers in health and social care. London: NICE, 2006.
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Nutrition support in adults: Oral nutrition support, enteral tube feeding and parenteral nutrition. London: NICE, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Department of Constitutional Affairs. Mental Capacity Act Code of Practice. Norwich: Stationery Office, 2007.
-
- Young J, Inouye SK. Delirium in older people. BMJ 2007;334:842–6.10.1136/bmj.39169.706574.AD - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical