Low-dose metronomic chemotherapy with cisplatin: can it suppress angiogenesis in H22 hepatocarcinoma cells?
- PMID: 20096070
- PMCID: PMC2812723
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2009.00684.x
Low-dose metronomic chemotherapy with cisplatin: can it suppress angiogenesis in H22 hepatocarcinoma cells?
Abstract
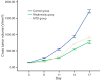
Low-dose chemotherapy drugs can suppress tumours by restraining tumour vessel growth and preventing the repair of damaged vascular endothelial cells. Cisplatin is a broad-spectrum, cell cycle-non-specific drug, but has serious side effects if used at high doses. There have been few reports on the anti-angiogenic effects of low-dose cisplatin and hence the effect of low-dose metronomic (LDM) chemotherapy on the proliferation and neovascularization of H22 hepatocarcinoma cells is discussed in this research. The influence of LDM chemotherapy with cisplatin on human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs) and proliferation of the HepG(2) human hepatocarcinoma cell line were measured using MTT assays. The LDM group was treated with cisplatin 0.6 mg/kg/day; the control group with saline 0.2 ml; the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) group with cisplatin 9 mg/kg/day. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix metallopeptidase 2 (MMP-2) were detected using immunohistochemical staining. A chicken chorio-allantoic membrane (CAM) model was used to check the inhibitory effect of LDM chemotherapy with cisplatin on neovascularization in vivo. Low-dose cisplatin inhibited HUVEC proliferation in a dose- and time-dependent manner, but was ineffective in inhibiting HepG(2) cell proliferation. Tumour growth was delayed in mice receiving LDM cisplatin, without apparent body weight loss, compared with mice that received MTD cisplatin. Microvessel density and expression of VEGF and MMP-2 were much lower in mice receiving LDM cisplatin than in the control and MTD groups. Continuous low-dose cisplatin suppressed CAM angiogenesis in vivo. LDM chemotherapy with cisplatin can inhibit the growth of blood vessel endothelial cells in vitro and shows anti-angiogenic ability in vivo.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The epigallocatechin gallate derivative Y6 inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting angiogenesis in MAPK/ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT/ HIF-1α/VEGF dependent pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Sep 15;259:112852. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112852. Epub 2020 Apr 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32278759
-
FP3: a novel VEGF blocker with anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor effects.Hepatogastroenterology. 2012 Nov-Dec;59(120):2543-7. doi: 10.5754/hge12159. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22534543
-
Metronomic gemcitabine targeted tumor vascular microenvironment decreases the population of CD133(+) cells in hepatocarcinoma xenografts.Cancer Biomark. 2014;14(6):427-33. doi: 10.3233/CBM-140419. Cancer Biomark. 2014. PMID: 25335734
-
Metronomic chemotherapy and anti-angiogenesis: can upgraded pre-clinical assays improve clinical trials aimed at controlling tumor growth?APMIS. 2014 Jul;122(7):565-79. doi: 10.1111/apm.12201. Epub 2013 Oct 26. APMIS. 2014. PMID: 24164171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A critical analysis of current in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis assays.Int J Exp Pathol. 2009 Jun;90(3):195-221. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2008.00633.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19563606 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metronomic chemotherapy: possible clinical application in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Transl Oncol. 2013 Oct 1;6(5):511-9. doi: 10.1593/tlo.13481. eCollection 2013. Transl Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24151531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antitumor and immunomodulatory effects of low-dose 5-FU on hepatoma 22 tumor-bearing mice.Oncol Lett. 2014 Apr;7(4):1260-1264. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.1856. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24660037 Free PMC article.
-
Low dosages: new chemotherapeutic weapons on the battlefield of immune-related disease.Cell Mol Immunol. 2011 Jul;8(4):289-95. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2011.6. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Cell Mol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21423201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorescence monitoring of hypoxic microenvironment in solid-tumors to evaluate chemotherapeutic effects using the hypoxia-sensitive iridium (III) coordination compound.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 18;10(3):e0121293. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121293. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25786221 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral Treatment in Lung Cancer: Is It Time to Move Towards Clinical Practice?Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 21;16(23):3892. doi: 10.3390/cancers16233892. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albertsson P, Lennernäs B, Norrby K. On metronomic chemotherapy: modulation of angiogenesis mediated by VEGE-A. Acta Oncol. 2006;45:144–155. - PubMed
-
- Assaraf YG. The role of multidrug resistance efflux transporters in antifolate resistance and folate homeostasis. Drug Resist. Updat. 2006;9:227–246. - PubMed
-
- Buckstein R, Kerbel RS, Shaked Y, et al. High-dose celecoxib and metronomic “low-dose” cyclophosphamide is an effective and safe therapy in patients with relapsed and refractory aggressive histology non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006;12:5190–5198. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis and apoptosis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2003;13:159–167. - PubMed
-
- Franchi F, Grassi P, Ferro D, et al. Antiangiogenic metronomic chemotherapy and hyperthermia in the palliation of advanced cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Care. 2007;16:258–262. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

