Comparison of the epidermal growth factor receptor protein expression between primary non-small cell lung cancer and paired lymph node metastases: implications for targeted nuclide radiotherapy
- PMID: 20096104
- PMCID: PMC2830952
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-7
Comparison of the epidermal growth factor receptor protein expression between primary non-small cell lung cancer and paired lymph node metastases: implications for targeted nuclide radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: The knowledge of Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression in metastases of NSCLC was limited. In receptor-mediated targeted nuclide radiotherapy, tumor cells are killed with delivered radiation and therapeutic efficiency is mainly dependent on the receptor expression. Thus, the level and stability of receptor expression in both primary tumors and corresponding metastases is crucial in the assessment of a receptor as target. The goal of this study was to evaluate whether EGFR is suitable as target for clinical therapy.
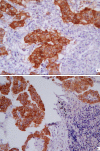
Methods: Expression of EGFR was investigated immunohistochemically in paired samples of lymph node metastases and corresponding NSCLC primary lesions (n = 51). EGFR expression was scored as 0, 1+, 2+ or 3+.
Results: Positive (1+, 2+ or 3+) EGFR immunostaining was evident in 36 of 47 (76.6%) analysed NSCLC primary tumors, and in 78.7% of the corresponding lymph node metastases. When EGFR expression is classified as positive or negative, discordance between the primary tumors and the corresponding metastases was observed in 5 cases (10.6%). EGFR overexpression (2+ or 3+) was found in 53.2% (25/47) of the NSCLC primary tumors and 59.6% of the corresponding metastases. Nine out of the 47 paired samples (19.2%) were discordant: Only three patients who had EGFR overexpression in the primary tumors showed EGFR downregulation (0 or 1+) in lymph node metastases, while six patients changed the other way around.
Conclusions: The EGFR expression in the primary tumor and the corresponding metastasis is discordant in about 10% of the patients. When overexpression is considered, the discordance is observed in about 20% of the cases. However, concerning EGFR overexpression in the primary tumors, similar expression in the metastases could be predicted with a reasonably high probability, which is encouraging for testing of EGFR targeted nuclide radiotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EGFR and HER2 expression in primary cervical cancers and corresponding lymph node metastases: implications for targeted radiotherapy.BMC Cancer. 2008 Aug 12;8:232. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-8-232. BMC Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18700025 Free PMC article.
-
Discordance of molecular biomarkers associated with epidermal growth factor receptor pathway between primary tumors and lymph node metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2009 Jul;4(7):809-15. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181a94af4. J Thorac Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19487967
-
EGFR, HER2, and HER3 expression in laryngeal primary tumors and corresponding metastases.Ann Surg Oncol. 2008 Apr;15(4):1193-201. doi: 10.1245/s10434-007-9771-3. Epub 2008 Jan 3. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18172732
-
Discordance of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation between primary lung tumor and paired distant metastases in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 19;14(6):e0218414. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218414. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31216329 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor and KRAS gene status between primary and corresponding metastatic tumours of non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2015 Jan;27(1):30-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2015. PMID: 25445553 Review.
Cited by
-
-216G/T (rs712829), a functional variant of the EGFR promoter, is associated with the pleural metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2013 Sep;6(3):693-698. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1442. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 24137392 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of EGFR and KRAS status between primary non-small cell lung cancer and corresponding metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2010 Sep;13(9):882-91. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2010.09.09. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20840818 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Correlation study and significance of the EGFR expression in serum, lymph nodes and tumor tissue of NSCLC.Thorac Cancer. 2014 Jan;5(1):31-7. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12048. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Thorac Cancer. 2014. PMID: 26766969 Free PMC article.
-
[Advances of heterogeneity of EGFR in non-small cell lung cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2011 Nov;14(11):890-3. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2011.11.11. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22104226 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
-
Correlations between EGFR gene polymorphisms and pleural metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Aug 25;9:5257-70. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S97907. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27601918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ihde DC. Chemotherapy of lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:1434–1441. - PubMed
-
- Pfister DG, Johnson DH, Azzoli CG, Sause W, Smith TJ, Baker S Jr, Olak J, Stover D, Strawn JR, Turrisi AT, Somerfield MR. American Society of Clinical Oncology. American Society of Clinical Oncology treatment of unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer guideline: update 2003. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:330–353. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.09.053. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous