ABL-N-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells is partially mediated by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation
- PMID: 20096139
- PMCID: PMC2880430
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2475
ABL-N-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells is partially mediated by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation
Abstract
Introduction: The present study was designed to determine the possibility of acetylbritannilactone (ABL) derivative 5-(5-(ethylperoxy)pentan-2-yl)-6-methyl-3-methylene-2-oxo-2,3,3a,4,7,7a-hexahydrobenzofuran-4-yl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate (ABL-N) as a novel therapeutic agent in human breast cancers.
Methods: We investigated the effects of ABL-N on the induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells and further examined the underlying mechanisms. Moreover, tumor growth inhibition of ABL-N was done in xenograft models.
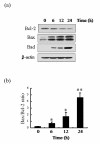
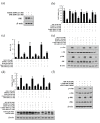
Results: ABL-N induced the activation of caspase-3 in estrogen receptor (ER)-negative cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468, as evidenced by the cleavage of endogenous substrate Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). Pretreatment of cells with pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk or caspase-3-specific inhibitor z-DEVD-fmk inhibited ABL-N-induced apoptosis. ABL-N treatment also resulted in an increase in the expression of pro-apoptotic members (Bax and Bad) with a concomitant decrease in Bcl-2. Furthermore, c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase (p38) were activated in the apoptosis induced by ABL-N and JNK-specific inhibitor SP600125 and JNK small interfering RNA (siRNA) antagonized ABL-N-mediated apoptosis. However, the p38-specific inhibitor SB203580 had no effect upon these processes. Moreover, neither of the caspase inhibitors prevented ABL-N-induced JNK activation, indicating that JNK is upstream of caspases in ABL-N-initiated apoptosis. Additionally, in a nude mice xenograft experiment, ABL-N significantly inhibited the tumor growth of MDA-MB-231 cells.
Conclusions: ABL-N induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells through the activation of caspases and JNK signaling pathways. Moreover, ABL-N treatment causes a significant inhibition of tumor growth in vivo. Therefore, it is thought that ABL-N might be a potential drug for use in breast cancer prevention and intervention.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Activation of stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and p38 kinase in calphostin C-induced apoptosis requires caspase-3-like proteases but is dispensable for cell death.J Biol Chem. 1999 Feb 26;274(9):5310-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.9.5310. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10026138
-
JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) and p38 activation in receptor-mediated and chemically-induced apoptosis of T-cells: differential requirements for caspase activation.Biochem J. 2000 May 15;348 Pt 1(Pt 1):93-101. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10794718 Free PMC article.
-
Asiatic acid, a triterpene, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in human breast cancer cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Apr;313(1):333-44. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.078808. Epub 2004 Dec 30. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 15626723
-
The activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways protects HeLa cells from apoptosis following photodynamic therapy with hypericin.J Biol Chem. 1999 Mar 26;274(13):8788-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.13.8788. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10085120
-
Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development.Nat Rev Cancer. 2009 Aug;9(8):537-49. doi: 10.1038/nrc2694. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19629069 Review.
Cited by
-
PCAT-1 facilitates breast cancer progression via binding to RACK1 and enhancing oxygen-independent stability of HIF-1α.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Mar 3;24:310-324. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.02.034. eCollection 2021 Jun 4. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 33850635 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on antitumor mechanisms and molecular targets of Inula sesquiterpene lactones.Chin Med. 2023 Dec 18;18(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00870-1. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 38111074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inula L. Secondary Metabolites against Oxidative Stress-Related Human Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 May 6;8(5):122. doi: 10.3390/antiox8050122. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31064136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, Characterization, and Anticancer Activity of New N,N'-Diarylthiourea Derivative against Breast Cancer Cells.Molecules. 2023 Sep 3;28(17):6420. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176420. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687250 Free PMC article.
-
The WNT10B Network Is Associated with Survival and Metastases in Chemoresistant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancer Res. 2019 Mar 1;79(5):982-993. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1069. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30563890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garcia-Carbonero R, Supko JG. Current perspectives on the clinical experience, pharmacology, and continued development of the camptothecins. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:641–661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

