Toward better management of merkel cell carcinoma using a consensus staging system, new diagnostic codes and a recently discovered virus
- PMID: 20096162
- PMCID: PMC9439968
- DOI: 10.1016/s0001-7310(09)73378-2
Toward better management of merkel cell carcinoma using a consensus staging system, new diagnostic codes and a recently discovered virus
Abstract
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a neuroendocrine skin cancer with a higher propensity for recurrence and metastasis than melanoma or squamous cell carcinoma. Despite aggressive behavior and the tripling of its reported incidence in the past 20 years, there is extensive confusion about how MCC should be managed. Here we address two issues that have impeded optimal MCC management: lack of a consensus staging system and lack of unique diagnostic codes for MCC. Five conflicting systems currently used to stage MCC will be replaced by one system in 2010 that will diminish confusion about prognosis and management among physicians and patients. The diagnostic bundling of MCC with numerous less aggressive skin cancers leads to care refusals by insurance and an inability to track MCC care costs. Worldwide adoption in 2009 of specific diagnostic codes for MCC will also improve understanding and management of this often-lethal skin cancer.
El carcinoma de células de Merkel (CCM) es una neoplasia cutánea neuroendocrina con una mayor propensión para desarrollar recurrencias y metástasis que el melanoma o el carcinoma epidermoide. A pesar de su comportamiento agresivo, y el hecho de que su incidencia se haya triplicado en los últimos 20 años, aún existe una gran confusión respecto al tratamiento del CCM. En esta revisión abordaremos dos cuestiones que han dificultado el tratamiento óptimo del CCM: la carencia de un sistema de estadificación consensuado y la falta de códigos diagnósticos exclusivos para el CCM. Los 5 sistemas contradictorios que actualmente se utilizan para estadificar el CCM serán reemplazados solamente por uno en 2010, lo que disminuirá la confusión sobre el pronóstico y el tratamiento entre los médicos y pacientes. La codificación diagnóstica del CCM, junto con numerosas neoplasias cutáneas menos agresivas, ha condicionado la denegación de atención por parte de las compañías aseguradoras y la incapacidad para evaluar los costes de la atención sanitaria por CCM.
La adopción, que se ha efectuado en 2009, de códigos diagnósticos específicos para el CCM también mejorará la comprensión y el tratamiento de esta neoplasia cutánea frecuentemente letal.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
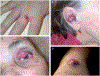
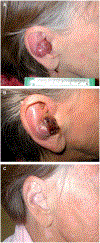
References
-
- Agelli M, Clegg LX. Epidemiology of primary Merkel cell carcinoma in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:832–41. - PubMed
-
- Balch CM, Soong SJ, Gershenwald JE, Thompson JF, Reintgen DS, Cascinelli N, et al. Prognostic factors analysis of 17,600 melanoma patients: validation of the American Joint Committee on Cancer melanoma staging system. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:3622–34. - PubMed
-
- Goggins W, Daniels GH, Tsao H. Elevation of thyroid cancer risk among cutaneous melanoma survivors. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:185–8. - PubMed
-
- Lens MB, Dawes M, Newton-Bishop JA, Goodacre T. Tumour thickness as a predictor of occult lymph node metastases in patients with stage I and II melanoma undergoing sentinel lymph node biopsy. Br J Surg. 2002;89:1223–7. - PubMed
-
- Gupta SG, Wang LC, Peñas PF, Gellenthin M, Lee SJ, Nghiem P. Sentinel lymph node biopsy for evaluation and treatment of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma: The Dana-Farber experience and meta-analysis of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:685–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
