Alterations in brain antioxidant enzymes and redox proteomic identification of oxidized brain proteins induced by the anti-cancer drug adriamycin: implications for oxidative stress-mediated chemobrain
- PMID: 20096337
- PMCID: PMC2852883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.01.021
Alterations in brain antioxidant enzymes and redox proteomic identification of oxidized brain proteins induced by the anti-cancer drug adriamycin: implications for oxidative stress-mediated chemobrain
Abstract
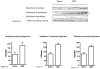
Adriamycin (ADR) is a chemotherapeutic for the treatment of solid tumors. This quinone-containing anthracycline is well known to produce large amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in vivo. A common complaint of patients undergoing long-term treatment with ADR is somnolence, often referred to as "chemobrain." While ADR itself does not cross the blood brain barrier (BBB), we recently showed that ADR administration causes a peripheral increase in tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), which migrates across the BBB and leads to inflammation and oxidative stress in brain, most likely contributing to the observed decline in cognition. In the current study, we measured levels of the antioxidant glutathione (GSH) in brains of mice injected intraparitoneally (i.p.) with ADR, as well as the levels and activities of several enzymes involved in brain GSH metabolism. We observed significantly decreased GSH levels, as well as altered GSH/GSSG ratio in brains of ADR treated mice relative to saline-treated controls. Also observed in brains of ADR treated mice were increased levels of glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), and glutathione reductase (GR). We also observed increased activity of GPx, but a significant reduction in GST and GR activity in mice brain, 72 h post i.p. injection of ADR (20 mg/kg body weight). Furthermore, we used redox proteomics to identify specific proteins that are oxidized and/or have differential levels in mice brains as a result of a single i.p. injection of ADR. Visinin like protein 1 (VLP1), peptidyl prolyl isomerase 1 (Pin1), and syntaxin 1 (SYNT1) showed differential levels in ADR treated mice relative to saline-treated controls. Triose phosphate isomerase (TPI), enolase, and peroxiredoxin 1 (PRX-1) showed significantly increased specific carbonylation in ADR treated mice brain. These results further support the notion ADR induces oxidative stress in brain despite not crossing the BBB, and that antioxidant intervention may prevent ADR-induced cognitive dysfunction.
Copyright 2010 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Glutathione elevation by gamma-glutamyl cysteine ethyl ester as a potential therapeutic strategy for preventing oxidative stress in brain mediated by in vivo administration of adriamycin: Implication for chemobrain.J Neurosci Res. 2007 Feb 15;85(3):497-503. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21158. J Neurosci Res. 2007. PMID: 17171703
-
Free radical mediated oxidative stress and toxic side effects in brain induced by the anti cancer drug adriamycin: insight into chemobrain.Free Radic Res. 2005 Nov;39(11):1147-54. doi: 10.1080/10715760500143478. Free Radic Res. 2005. PMID: 16298740
-
Prophylactic effect of lipoic acid against adriamycin-induced peroxidative damages in rat kidney.Ren Fail. 2003 May;25(3):367-77. doi: 10.1081/jdi-120021151. Ren Fail. 2003. PMID: 12803501
-
Chemobrain in rats: Behavioral, morphological, oxidative and inflammatory effects of doxorubicin administration.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Jan 27;378:112233. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112233. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31521736
-
Oxidative stress in traumatic brain injury.Curr Med Chem. 2014 Apr;21(10):1201-11. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666131217153310. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24350853 Review.
Cited by
-
Senolytic treatment alleviates doxorubicin-induced chemobrain.Aging Cell. 2024 Feb;23(2):e14037. doi: 10.1111/acel.14037. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38225896 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Potential of Ellagic Acid: A Critical Review.Adv Nutr. 2021 Jul 30;12(4):1211-1238. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab007. Adv Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33693510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth of Triple Negative and Progesterone Positive Breast Cancer Causes Oxidative Stress and Down-Regulates Neuroprotective Transcription Factor NPAS4 and NPAS4-Regulated Genes in Hippocampal Tissues of TumorGraft Mice-an Aging Connection.Front Genet. 2018 Mar 5;9:58. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00058. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 29556248 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive effects of cancer and its treatments at the intersection of aging: what do we know; what do we need to know?Semin Oncol. 2013 Dec;40(6):709-25. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2013.09.006. Semin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24331192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cisplatin-induced mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with impaired cognitive function in rats.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Jan;102:274-286. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.046. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 27908784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ames JB, Ishima R, Tanaka T, Gordon JI, Stryer L, Ikura M. Molecular mechanics of calcium-myristoyl switches. Nature. 1997;389:198–202. - PubMed
-
- Benzi G, Moretti A. Age- and peroxidative stress-related modifications of the cerebral enzymatic activities linked to mitochondria and the glutathione system. Free radical biology & medicine. 1995;19:77–101. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein HG, Baumann B, Danos P, Diekmann S, Bogerts B, Gundelfinger ED, Braunewell KH. Regional and cellular distribution of neural visinin-like protein immunoreactivities (VILIP-1 and VILIP-3) in human brain. Journal of neurocytology. 1999;28:655–662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

