Early and late administration of MnTE-2-PyP5+ in mitigation and treatment of radiation-induced lung damage
- PMID: 20096348
- PMCID: PMC3704177
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.01.020
Early and late administration of MnTE-2-PyP5+ in mitigation and treatment of radiation-induced lung damage
Abstract
Chronic production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species is an underlying mechanism of irradiation (IR)-induced lung injury. The purpose of this study was to determine the optimum time of delivery of an antioxidant and redox-modulating Mn porphyrin, MnTE-2-PyP(5+), to mitigate and/or treat IR-induced lung damage. Female Fischer-344 rats were irradiated to their right hemithorax (28 Gy). Irradiated animals were treated with PBS or MnTE-2-PyP(5+) (6 mg /kg/24 h) delivered for 2 weeks by sc-implanted osmotic pumps (beginning after 2, 6, 12, 24, or 72 h or 8 weeks). Animals were sacrificed 10 weeks post-IR. Endpoints were body weight, breathing frequency, histopathology, and immunohistochemistry (8-OHdG, ED-1, TGF-beta, HIF-1alpha, VEGF A). A significant radioprotective effect on functional injury, measured by breathing frequency, was observed for all animals treated with MnTE-2-PyP(5+). Treatment with MnTE-2-PyP(5+) starting 2, 6, and 12 h but not after 24 or 72 h resulted in a significant decrease in immunostaining for 8-OHdG, HIF-1alpha, TGF-beta, and VEGF A. A significant decrease in HIF-1alpha, TGF-beta, and VEGF A, as well as an overall reduction in lung damage (histopathology), was observed in animals beginning treatment at the time of fully developed lung injury (8 weeks post-IR). The catalytic manganese porphyrin antioxidant and modulator of redox-based signaling pathways MnTE-2-PyP(5+) mitigates radiation-induced lung injury when given within the first 12 h after IR. More importantly, this is the first study to demonstrate that MnTE-2-PyP(5+) can reverse overall lung damage when started at the time of established lung injury 8 weeks post-IR. The radioprotective effects are presumably mediated through its ability both to suppress oxidative stress and to decrease activation of key transcription factors and proangiogenic and profibrogenic cytokines.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


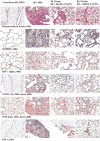
Similar articles
-
Robust rat pulmonary radioprotection by a lipophilic Mn N-alkylpyridylporphyrin, MnTnHex-2-PyP(5+).Redox Biol. 2014 Jan 9;2:400-10. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.12.017. eCollection 2014. Redox Biol. 2014. PMID: 24624330 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of two Mn porphyrin-based mimics of superoxide dismutase in pulmonary radioprotection.Free Radic Biol Med. 2008 Mar 15;44(6):982-9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.10.058. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008. PMID: 18082148 Free PMC article.
-
Superoxide dismutase mimic, MnTE-2-PyP(5+) ameliorates acute and chronic proctitis following focal proton irradiation of the rat rectum.Redox Biol. 2013 Oct 25;1(1):599-607. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.10.002. eCollection 2013. Redox Biol. 2013. PMID: 24363995 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse functions of cationic Mn(III) N-substituted pyridylporphyrins, recognized as SOD mimics.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Sep 1;51(5):1035-53. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.04.046. Epub 2011 May 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21616142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of Mn porphyrins for treating oxidative stress injuries and their redox-based regulation of cellular transcriptional activities.Amino Acids. 2012 Jan;42(1):95-113. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0603-6. Epub 2010 May 16. Amino Acids. 2012. PMID: 20473774 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitigation of Radiation-Induced Lung Pneumonitis and Fibrosis Using Metformin and Melatonin: A Histopathological Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Jul 30;55(8):417. doi: 10.3390/medicina55080417. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31366142 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species Drive Epigenetic Changes in Radiation-Induced Fibrosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Feb 6;2019:4278658. doi: 10.1155/2019/4278658. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 30881591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feasibility study for inducing the skeletal muscle fibrosis via irradiation using two mouse strains.Jpn J Radiol. 2022 May;40(5):466-475. doi: 10.1007/s11604-021-01219-0. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Jpn J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34841459
-
Late administration of Mn porphyrin-based SOD mimic enhances diabetic complications.Redox Biol. 2013 Sep 20;1(1):457-66. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.09.005. eCollection 2013. Redox Biol. 2013. PMID: 24191241 Free PMC article.
-
Balanced Duality: H2O2-Based Therapy in Cancer and Its Protective Effects on Non-Malignant Tissues.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 15;25(16):8885. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168885. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201571 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vujaskovic Z, Anscher MS, Feng QF, Rabbani ZN, Amin K, Samulski TS, Dewhirst MW, Haroon ZA. Radiation-induced hypoxia may perpetuate late normal tissue injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;50:851–855. - PubMed
-
- Mikkelsen RB, Wardman P. Biological chemistry of reactive oxygen and nitrogen and radiation-induced signal transduction mechanisms. Oncogene. 2003;22:5734–5754. - PubMed
-
- Leach JK, Van Tuyle G, Lin PS, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Mikkelsen RB. Ionizing radiation-induced, mitochondria-dependent generation of reactive oxygen/nitrogen. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3894–3901. - PubMed
-
- Pearce LL, Epperly MW, Greenberger JS, Pitt BR, Peterson J. Identification of respiratory complexes I and III as mitochondrial sites of damage following exposure to ionizing radiation and nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide. 2001;5:128–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

