Decreased BDNF in patients with antipsychotic naïve first episode schizophrenia
- PMID: 20096541
- PMCID: PMC2868956
- DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2009.12.035
Decreased BDNF in patients with antipsychotic naïve first episode schizophrenia
Abstract
Objective: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a key factor known to mediate neuronal proliferation, differentiation, survival and response to stress. Decreases in BDNF levels have been reported in schizophrenia, but studies in treatment naïve patients are few. Herein we report on serum BDNF levels in a series of patients with first-episode treatment naïve psychoses in comparison to age matched healthy controls.
Method: Fasting serum BDNF levels were measured in 41 patients with treatment naive first episode psychosis (24 with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder or schizophreniform disorder, and 17 with non-schizophrenia psychotic disorders) and 41 age-matched healthy controls.
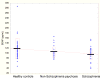
Results: A three group analyses of covariance (ANCOVA) showed a diagnosis effect (p=.038) in which patients with schizophrenia had lesser serum BDNF levels than patient with non-schizophrenia psychosis, who in turn had lesser BDNF levels than matched healthy controls. Planned two-group ANCOVAs suggested that patients with schizophrenia had lower serum BDNF level than matched controls (p=.016), whereas patients with non-schizophrenia psychosis did not differ from controls. There were no age effects on BDNF, but there was a trend (p=.08) for a gender by group interaction with greater reductions in female patients with schizophrenia. The BDNF levels did not correlate with magnitude of smoking, body mass index, severity of positive and negative symptoms or overall functioning.
Conclusions: Serum BDNF may be reduced at the onset of psychosis but its role in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia remains unclear. Elucidating the role of BDNF in schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders may provide an important therapeutic target. Further studies are also needed to examine if patients with schizophrenia have more pronounced reductions in BDNF than those with affective psychosis.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Altar CA, Cai N, Bliven T, Juhasz M, Conner JM, Acheson AL, et al. Anterograde transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its role in the brain. Nature. 1997;389:856–860. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press; 1994.
-
- Andreasen NC. Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS) Iowa City: IA: University of Iowa; 1983.
-
- Andreasen NC. Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms (SAPS) Iowa City: IA: University of Iowa; 1984.
-
- Angelucci F, Aloe L, Iannitelli A, Gruber SH, Mathe AA. Effect of chronic olanzapine treatment on nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rat brain. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2005;15:311–317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical