The first low microM SecA inhibitors
- PMID: 20096592
- PMCID: PMC2828495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.12.074
The first low microM SecA inhibitors
Abstract
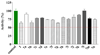
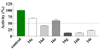
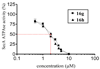
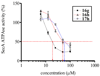
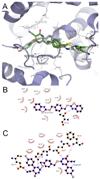
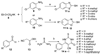
SecA ATPase is a critical member of the Sec family, which is important in the translocation of membrane and secreted polypeptides/proteins in bacteria. Small molecule inhibitors can be very useful research tools as well as leads for future antimicrobial agent development. Based on previous virtual screening work, we optimized the structures of two hit compounds and obtained SecA ATPase inhibitors with IC(50) in the single digit micromolar range. These represent the first low micromolar synthetic inhibitors of bacterial SecA and will be very useful for mechanistic studies.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


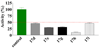



Similar articles
-
Fluorescein analogues inhibit SecA ATPase: the first sub-micromolar inhibitor of bacterial protein translocation.ChemMedChem. 2012 Apr;7(4):571-7. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201100594. Epub 2012 Feb 22. ChemMedChem. 2012. PMID: 22354575 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of the first SecA inhibitors using structure-based virtual screening.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Apr 18;368(4):839-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.01.135. Epub 2008 Feb 7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18261984
-
Evaluation of small molecule SecA inhibitors against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Bioorg Med Chem. 2015 Nov 1;23(21):7061-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.09.027. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26432604 Free PMC article.
-
SecA inhibitors as potential antimicrobial agents: differential actions on SecA-only and SecA-SecYEG protein-conducting channels.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018 Aug 1;365(15):fny145. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fny145. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30007321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SecA: a potential antimicrobial target.Future Med Chem. 2015;7(8):989-1007. doi: 10.4155/fmc.15.42. Future Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26062397 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of small-molecule inhibitors against SecA by structure-based virtual ligand screening.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2015 Nov;68(11):666-73. doi: 10.1038/ja.2015.53. Epub 2015 May 20. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2015. PMID: 25990955
-
Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of Triazole-Pyrimidine Analogues as SecA Inhibitors.ChemMedChem. 2016 Jan 5;11(1):43-56. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201500447. Epub 2015 Nov 26. ChemMedChem. 2016. PMID: 26607404 Free PMC article.
-
Novel cyanothiouracil and cyanothiocytosine derivatives as concentration-dependent selective inhibitors of U87MG glioblastomas: Adenosine receptor binding and potent PDE4 inhibition.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Feb 15;212:113125. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.113125. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33422981 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and bioactivity evaluation of new 6-aryl-5-cyano thiouracils as potential antimicrobial and anticancer agents.Molecules. 2012 Aug 17;17(8):9868-86. doi: 10.3390/molecules17089868. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 22902882 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Rose Bengal inhibition on SecA ATPase and ion channel activities.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Nov 14;454(2):308-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.10.070. Epub 2014 Oct 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25450394 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

