Autophagy in cellular growth control
- PMID: 20096689
- PMCID: PMC2856449
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.01.009
Autophagy in cellular growth control
Abstract
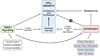
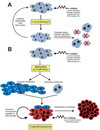
Cell growth is regulated by two antagonistic processes: TOR signaling and autophagy. These processes integrate signals including growth factors, amino acids, and energy status to ensure that cell growth is appropriate to environmental conditions. Autophagy responds indirectly to the cellular milieu as a downstream inhibitory target of TOR signaling and is also directly controlled by nutrient availability, cellular energy status, and cell stress. The control of cell growth by TOR signaling and autophagy are relevant to disease, as altered regulation of either pathway results in tumorigenesis. Here we give an overview of how TOR signaling and autophagy integrate nutritional status to regulate cell growth, how these pathways are coordinately regulated, and how dysfunction of this regulation might result in tumorigenesis.
Copyright 2010 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ahn CH, Jeong EG, Lee JW, Kim MS, Kim SH, Kim SS, Yoo NJ, Lee SH. Expression of beclin-1, an autophagy-related protein, in gastric and colorectal cancers. APMIS. 2007;115:1344–1349. - PubMed
-
- Aita VM, Liang XH, Murty VV, Pincus DL, Yu W, Cayanis E, Kalachikov S, Gilliam TC, Levine B. Cloning and genomic organization of beclin 1, a candidate tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 17q21. Genomics. 1999;59:59–65. - PubMed
-
- Arico S, Petiot A, Bauvy C, Dubbelhuis PF, Meijer AJ, Codogno P, Ogier-Denis E. The tumor suppressor PTEN positively regulates macroautophagy by inhibiting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:35243–35246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

