Therapeutic strategies underpinning the development of novel techniques for the treatment of HIV infection
- PMID: 20096804
- PMCID: PMC2910421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.01.004
Therapeutic strategies underpinning the development of novel techniques for the treatment of HIV infection
Abstract
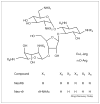
The HIV replication cycle offers multiple targets for chemotherapeutic intervention, including the viral exterior envelope glycoprotein, gp120; viral co-receptors CXCR4 and CCR5; transmembrane glycoprotein, gp41; integrase; reverse transcriptase; protease and so on. Most currently used anti-HIV drugs are reverse transcriptase inhibitors or protease inhibitors. The expanding application of simulation to drug design combined with experimental techniques have developed a large amount of novel inhibitors that interact specifically with targets besides transcriptase and protease. This review presents details of the anti-HIV inhibitors discovered with computer-aided approaches and provides an overview of the recent five-year achievements in the treatment of HIV infection and the application of computational methods to current drug design.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Girard MP, et al. A review of vaccine research and development: the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Vaccine. 2006;24:4062–4081. - PubMed
-
- Barbaro G, et al. Highly active antiretroviral therapy: current state of the art, new agents and their pharmacological interactions useful for improving therapeutic outcome. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11:1805–1843. - PubMed
-
- Louie M, Markowitz M. Goals and milestones during treatment of HIV-1 infection with antiretroviral therapy: a pathogenesis-based perspective. Antiviral Res. 2002;55:15–25. - PubMed
-
- Greene WC. The brightening future of HIV therapeutics. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:867–871. - PubMed
-
- Hazuda D, et al. Emerging pharmacology: inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus integration. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2009;49:377–394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

