Drug screening for hearing loss: using the zebrafish lateral line to screen for drugs that prevent and cause hearing loss
- PMID: 20096805
- PMCID: PMC2912212
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.01.001
Drug screening for hearing loss: using the zebrafish lateral line to screen for drugs that prevent and cause hearing loss
Abstract
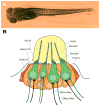
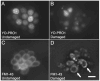
Several animal models have been used for the study of mechanosensory hair cells and hearing loss. Because of the difficulty of tissue acquisition and large animal size, these traditional models are impractical for high-throughput screening. The zebrafish has emerged as a powerful animal model for screening drugs that cause and prevent hair cell death. The unique characteristics of the zebrafish enable rapid in vivo imaging of hair cells and hair cell death. We have used this model to screen for and identify multiple drugs that protect hair cells from aminoglycoside-induced death. The identification of multiple drugs and drug-like compounds that inhibit multiple hair cell death pathways might enable the development of protective cocktails to achieve complete hair cell protection.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of small molecule inhibitors of cisplatin-induced hair cell death: results of a 10,000 compound screen in the zebrafish lateral line.Otol Neurotol. 2015 Mar;36(3):519-25. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000487. Otol Neurotol. 2015. PMID: 25687728 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical screening for hair cell loss and protection in the zebrafish lateral line.Zebrafish. 2010 Mar;7(1):3-11. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2009.0639. Zebrafish. 2010. PMID: 20192852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Fully Automated High-Throughput Zebrafish Behavioral Ototoxicity Assay.Zebrafish. 2017 Aug;14(4):331-342. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2016.1412. Epub 2017 May 18. Zebrafish. 2017. PMID: 28520533
-
Identification of FDA-approved drugs and bioactives that protect hair cells in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) lateral line and mouse (Mus musculus) utricle.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2009 Jun;10(2):191-203. doi: 10.1007/s10162-009-0158-y. Epub 2009 Feb 25. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2009. PMID: 19241104 Free PMC article.
-
Water Waves to Sound Waves: Using Zebrafish to Explore Hair Cell Biology.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2019 Feb;20(1):1-19. doi: 10.1007/s10162-018-00711-1. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30635804 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anion exchanger 1b in stereocilia is required for the functioning of mechanotransducer channels in lateral-line hair cells of zebrafish.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 13;10(2):e0117041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117041. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25679789 Free PMC article.
-
How Surrogate and Chemical Genetics in Model Organisms Can Suggest Therapies for Human Genetic Diseases.Genetics. 2018 Mar;208(3):833-851. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300124. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29487144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of ACSL4-Catalyzed Lipid Peroxidation Process Resists Cisplatin Ototoxicity.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Mar 20;2022:3080263. doi: 10.1155/2022/3080263. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35355868 Free PMC article.
-
Structure Characterization and Otoprotective Effects of a New Endophytic Exopolysaccharide from Saffron.Molecules. 2019 Feb 19;24(4):749. doi: 10.3390/molecules24040749. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30791463 Free PMC article.
-
PEPITA: Parallelized High-Throughput Quantification of Ototoxicity and Otoprotection in Zebrafish Larvae.Bio Protoc. 2024 Nov 5;14(21):e5105. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5105. eCollection 2024 Nov 5. Bio Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39525972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vio MM, Holme RH. Hearing loss and tinnitus: 250 million people and a US$10 billion potential market. Drug Discov Today. 2005;10:1263–1265. - PubMed
-
- Nadol JB, Jr, et al. Survival of spiral ganglion cells in profound sensorineural hearing loss: implications for cochlear implantation. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1989;98:411–416. - PubMed
-
- Nadol JB., Jr Patterns of neural degeneration in the human cochlea and auditory nerve: implications for cochlear implantation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997;117:220–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

