Transgenic inhibition of glial NF-kappa B reduces pain behavior and inflammation after peripheral nerve injury
- PMID: 20097004
- PMCID: PMC2853034
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.01.001
Transgenic inhibition of glial NF-kappa B reduces pain behavior and inflammation after peripheral nerve injury
Abstract
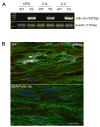
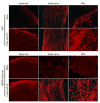
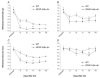
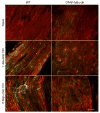
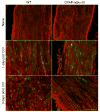
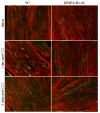
The transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) is a key regulator of inflammatory processes in reactive glial cells. We utilized a transgenic mouse model (GFAP-IkappaBalpha-dn) where the classical NF-kappaB pathway is inactivated by overexpression of a dominant negative (dn) form of the inhibitor of kappa B (IkappaBalpha) in glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-expressing cells, which include astrocytes, Schwann cells, and satellite cells of the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and sought to determine whether glial NF-kappaB inhibition leads to a reduction in pain behavior and inflammation following chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the sciatic nerve. As expected, following CCI nuclear translocation, and hence activation, of NF-kappaB was detected only in the sciatic nerve of wild type (WT) mice, and not in GFAP-IkappaBalpha-dn mice, while upregulation of GFAP was observed in the sciatic nerve and DRGs of both WT and GFAP-IkappaBalpha-dn mice, indicative of glial activation. Following CCI, mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia were reduced in GFAP-IkappaBalpha-dn mice compared to those in WT, as well as gene and protein expression of CCL2, CCR2 and CXCL10 in the sciatic nerve. Additionally, gene expression of TNF, CCL2, and CCR2 was reduced in the DRGs of transgenic mice compared to those of WT after CCI. We can therefore conclude that transgenic inhibition of NF-kappaB in GFAP-expressing glial cells attenuated pain and inflammation after peripheral nerve injury. These findings suggest that targeting the inflammatory response in Schwann cells and satellite cells may be important in treating neuropathic pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
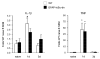
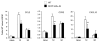
Similar articles
-
Glial NF-κB inhibition alters neuropeptide expression after sciatic nerve injury in mice.Brain Res. 2011 Apr 18;1385:38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.02.055. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21352816 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative effects of escin on neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;267:113503. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113503. Epub 2020 Oct 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33091488
-
Analgesic effects of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway inhibition on chronic neuropathic pain in rats following chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Nov;107:526-533. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.116. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. Retraction in: Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jul;163:114724. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114724. PMID: 30114636 Retracted.
-
Activation of NR2A-Wnt-TLR2 Signaling Axis in Satellite Glial Cells of the Dorsal Root Ganglion Contributes to Neuropathic Pain Induced by Nerve Injury in Diabetic Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun;62(6):8013-8037. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04754-3. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39964585
-
Gene expression changes in dorsal root ganglia following peripheral nerve injury: roles in inflammation, cell death and nociception.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Jun;14(6):939-947. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.250566. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30761997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exogenous TIPE2 Inhibit TAK1 to Improve Inflammation and Neuropathic Pain Induced by Sciatic Nerve Injury Through Inactivating NF-κB and JNK.Neurochem Res. 2022 Oct;47(10):3167-3177. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03671-4. Epub 2022 Jul 16. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35842555 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB in the mechanism of brain edema in acute liver failure: studies in transgenic mice.Neurobiol Dis. 2011 Feb;41(2):498-507. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2010.10.021. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Neurobiol Dis. 2011. PMID: 21087666 Free PMC article.
-
p75NTR is highly expressed in vestibular schwannomas and promotes cell survival by activating nuclear transcription factor κB.Glia. 2014 Oct;62(10):1699-712. doi: 10.1002/glia.22709. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Glia. 2014. PMID: 24976126 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathic pain-induced depressive-like behavior and hippocampal neurogenesis and plasticity are dependent on TNFR1 signaling.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Oct;41:65-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24938671 Free PMC article.
-
Discrepancy in the Usage of GFAP as a Marker of Satellite Glial Cell Reactivity.Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 16;9(8):1022. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9081022. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennett GJ, Xie YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 1988;33:87–107. - PubMed
-
- Campana WM, Li X, Shubayev VI, Angert M, Cai K, Myers RR. Erythropoietin reduces Schwann cell TNF-α, Wallerian degeneration and pain-related behaviors after peripheral nerve injury. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;23:617–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

