Alterations in molecular chaperones and eIF2alpha during lung endothelial cell apoptosis
- PMID: 20097734
- PMCID: PMC2853340
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00416.2009
Alterations in molecular chaperones and eIF2alpha during lung endothelial cell apoptosis
Abstract
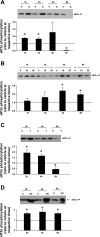
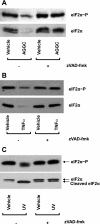
We have previously demonstrated that inhibition of CAAX carboxyl methylation with AGGC caused redistribution and condensation of the ER molecular chaperones, glucose-regulated protein (GRP)-94 and calnexin; an effect that was attenuated by overexpression of dominant active RhoA. We have also shown that AGGC decreased GRP94 protein level; an effect that was dependent on caspase activity. In the present study, we tested the effects of inhibition of posttranslational processing of CAAX proteins on localization and protein levels of molecular chaperones and phosphorylation and protein level of eIF2alpha. We found that both AGGC, which inhibits CAAX carboxyl methylation, and simvastatin, which inhibits CAAX geranylgeranylation, caused relocalization of GRP94, calnexin, and calreticulin, effects that were not seen during endothelial apoptosis induced by TNF-alpha or ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. These results suggest that posttranslational processing of CAAX proteins is important in maintaining localization of molecular chaperones normally found in the ER. We also noted that AGGC, but not simvastatin, TNF-alpha, or UV irradiation, decreased protein levels of most molecular chaperones. Increased eIF2alpha phosphorylation was observed in the early stages of apoptosis, which was independent of the cause of apoptosis. These results suggest that eIF2alpha phosphorylation is a common early response to apoptosis-inducing stimuli. Interestingly, eIF2alpha protein level was decreased in the late stages of apoptosis induced by AGGC, TNF-alpha, and UV irradiation: an effect that was prevented by caspase inhibition. Thus we speculate that caspase(s)-dependent proteolysis of molecular chaperones and eIF2alpha may be novel signaling pathways of apoptosis. We also speculate that increased eIF2alpha phosphorylation is a defensive response against endothelial cell apoptosis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibition of ICMT induces endothelial cell apoptosis through GRP94.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007 Jul;37(1):20-30. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0301SM. Epub 2007 Mar 8. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17347446 Free PMC article.
-
Ultraviolet light inhibits translation through activation of the unfolded protein response kinase PERK in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum.J Biol Chem. 2002 May 17;277(20):18077-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110164200. Epub 2002 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11877419
-
GCN2 phosphorylation of eIF2alpha activates NF-kappaB in response to UV irradiation.Biochem J. 2005 Jan 15;385(Pt 2):371-80. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041164. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15355306 Free PMC article.
-
eIF2α phosphorylation as a biomarker of immunogenic cell death.Semin Cancer Biol. 2015 Aug;33:86-92. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015. PMID: 25749194 Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum quality control and apoptosis.Acta Biochim Pol. 2005;52(2):381-95. Epub 2005 May 31. Acta Biochim Pol. 2005. PMID: 15933766 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome from Bone Marrow or Adipose-Derived Tissue Sources for Treatment of Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Epithelial Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 30;19(10):2996. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102996. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30274394 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Stress Response Mediates Epithelial Injury in Mechanical Ventilation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017 Aug;57(2):193-203. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0404OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28363030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bando Y, Katayama T, Aleshin AN, Manabe T, Tohyama M. GRP94 reduces cell death in SH-SY5Y cells perturbated calcium homeostasis. Apoptosis 9: 501–508, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Bergo MO, Leung GK, Ambroziak P, Otto JC, Casey PJ, Young SG. Targeted inactivation of the isoprenylcysteine carboxy methyltransferase gene causes mislocalization of K-Ras in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 275: 17605–17610, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Choy E, Chiu VK, Silletti J, Feoktistov M, Morimoto T, Michaelson D, Ivanov IE, Philips MR. Endomembrane trafficking of Ras: the CAAX motif targets proteins to the ER and Golgi. Cell 98: 69–80, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

