Role of transcription factor CaNdt80p in cell separation, hyphal growth, and virulence in Candida albicans
- PMID: 20097739
- PMCID: PMC2863402
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00325-09
Role of transcription factor CaNdt80p in cell separation, hyphal growth, and virulence in Candida albicans
Abstract
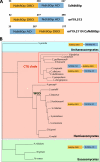
The NDT80/PhoG transcription factor family includes ScNdt80p, a key modulator of the progression of meiotic division in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In Candida albicans, a member of this family, CaNdt80p, modulates azole sensitivity by controlling the expression of ergosterol biosynthesis genes. We previously demonstrated that CaNdt80p promoter targets, in addition to ERG genes, were significantly enriched in genes related to hyphal growth. Here, we report that CaNdt80p is indeed required for hyphal growth in response to different filament-inducing cues and for the proper expression of genes characterizing the filamentous transcriptional program. These include noteworthy genes encoding cell wall components, such as HWP1, ECE1, RBT4, and ALS3. We also show that CaNdt80p is essential for the completion of cell separation through the direct transcriptional regulation of genes encoding the chitinase Cht3p and the cell wall glucosidase Sun41p. Consistent with their hyphal defect, ndt80 mutants are avirulent in a mouse model of systemic candidiasis. Interestingly, based on functional-domain organization, CaNdt80p seems to be a unique regulator characterizing fungi from the CTG clade within the subphylum Saccharomycotina. Therefore, this study revealed a new role of the novel member of the fungal NDT80 transcription factor family as a regulator of cell separation, hyphal growth, and virulence.
Figures
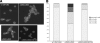





References
-
- Blackwell C., Russell C. L., Argimon S., Brown A. J., Brown J. D. 2003. Protein A-tagging for purification of native macromolecular complexes from Candida albicans. Yeast 20:1235–1241 - PubMed
-
- Butler G., Rasmussen M. D., Lin M. F., Santos M. A., Sakthikumar S., Munro C. A., Rheinbay E., Grabherr M., Forche A., Reedy J. L., Agrafioti I., Arnaud M. B., Bates S., Brown A. J., Brunke S., Costanzo M. C., Fitzpatrick D. A., de Groot P. W., Harris D., Hoyer L. L., Hube B., Klis F. M., Kodira C., Lennard N., Logue M. E., Martin R., Neiman A. M., Nikolaou E., Quail M. A., Quinn J., Santos M. C., Schmitzberger F. F., Sherlock G., Shah P., Silverstein K. A., Skrzypek M. S., Soll D., Staggs R., Stansfield I., Stumpf M. P., Sudbery P. E., Srikantha T., Zeng Q., Berman J., Berriman M., Heitman J., Gow N. A., Lorenz M. C., Birren B. W., Kellis M., Cuomo C. A. 2009. Evolution of pathogenicity and sexual reproduction in eight Candida genomes. Nature 459:657–662 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cabib E., Roberts R., Bowers B. 1982. Synthesis of the yeast cell wall and its regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 51:763–793 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

