The Aspergillus fumigatus P-type Golgi apparatus Ca2+/Mn2+ ATPase PmrA is involved in cation homeostasis and cell wall integrity but is not essential for pathogenesis
- PMID: 20097742
- PMCID: PMC2837981
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00378-09
The Aspergillus fumigatus P-type Golgi apparatus Ca2+/Mn2+ ATPase PmrA is involved in cation homeostasis and cell wall integrity but is not essential for pathogenesis
Abstract
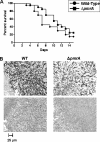
The Aspergillus fumigatus DeltapmrA (Golgi apparatus Ca(2+)/Mn(2+) P-type ATPase) strain has osmotically suppressible basal growth defects and cationic tolerance associated with increased expression of calcineurin pathway genes. Despite increased beta-glucan and chitin content, it is hypersensitive to cell wall inhibitors but remains virulent, suggesting a role for PmrA in cation homeostasis and cell wall integrity.
Figures



References
-
- Bates S., MacCallum D. M., Bertram G., Munro C. A., Hughes H. B., Buurman E. T., Brown A. J., Odds F. C., Gow N. A. 2005. Candida albicans Pmr1p, a secretory pathway P-type Ca2+/Mn2+-ATPase, is required for glycosylation and virulence. J. Biol. Chem. 280:23408–23415 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

