Drosophila octamer elements and Pdm-1 dictate the coordinated transcription of core histone genes
- PMID: 20097756
- PMCID: PMC2838325
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.075358
Drosophila octamer elements and Pdm-1 dictate the coordinated transcription of core histone genes
Abstract
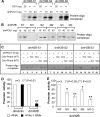
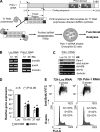
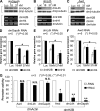
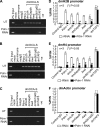
We reveal a set of divergent octamer elements in Drosophila melanogaster (dm) core histone gene promoters. These elements recruit transcription factor POU-domain protein in D. melanogaster 1 (Pdm-1), which along with co-activator dmOct-1 coactivator in S-phase (dmOCA-S), activates transcription from at least the Drosophila histone 2B (dmH2B) and 4 (dmH4) promoters in a fashion similar to the transcription of mammalian histone 2B (H2B) gene activated by octamer binding transcription factor 1 (Oct-1) and Oct-1 coactivator in S-phase (OCA-S). The expression of core histone genes in both kingdoms is coordinated; however, although the expression of mammalian histone genes involves subtype-specific transcription factors and/or co-activator(s), the expression of Drosophila core histone genes is regulated by a common module (Pdm-1/dmOCA-S) in a directly coordinated manner. Finally, dmOCA-S is recruited to the Drosophila histone locus bodies in the S-phase, marking S-phase-specific transcription activation of core histone genes.
Figures

References
-
- Roeder R. G. (2003) Nat. Med. 9, 1239–1244 - PubMed
-
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. (1981) Cell 25, 301–313 - PubMed
-
- Wang Z. F., Krasikov T., Frey M. R., Wang J., Matera A. G., Marzluff W. F. (1996) Genome Res. 6, 688–701 - PubMed
-
- Marzluff W. F., Duronio R. J. (2002) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14, 692–699 - PubMed
-
- Marzluff W. F., Gongidi P., Woods K. R., Jin J., Maltais L. J. (2002) Genomics 80, 487–498 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

