Hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1 is caused by the accumulation of two neurotoxic sphingolipids
- PMID: 20097765
- PMCID: PMC2856995
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.092973
Hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1 is caused by the accumulation of two neurotoxic sphingolipids
Abstract
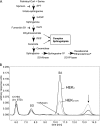
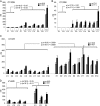
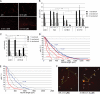
HSAN1 is an inherited neuropathy found to be associated with several missense mutations in the SPTLC1 subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT). SPT catalyzes the condensation of serine and palmitoyl-CoA, the initial step in the de novo synthesis of sphingolipids. Here we show that the HSAN1 mutations induce a shift in the substrate specificity of SPT, which leads to the formation of the two atypical deoxy-sphingoid bases (DSBs) 1-deoxy-sphinganine and 1-deoxymethyl-sphinganine. Both metabolites lack the C(1) hydroxyl group of sphinganine and can therefore neither be converted to complex sphingolipids nor degraded. Consequently, they accumulate in the cell, as demonstrated in HEK293 cells overexpressing mutant SPTLC1 and lymphoblasts of HSAN1 patients. Elevated DSB levels were also found in the plasma of HSAN1 patients and confirmed in three groups of HSAN1 patients with different SPTLC1 mutations. The DSBs show pronounced neurotoxic effects on neurite formation in cultured sensory neurons. The neurotoxicity co-occurs with a disturbed neurofilament structure in neurites when cultured in the presence of DSBs. Based on these observations, we conclude that HSAN1 is caused by a gain of function mutation, which results in the formation of two atypical and neurotoxic sphingolipid metabolites.
Figures


References
-
- Auer-Grumbach M., Mauko B., Auer-Grumbach P., Pieber T. R. (2006) Neuromolecular. Med. 8, 147–158 - PubMed
-
- Dawkins J. L., Hulme D. J., Brahmbhatt S. B., Auer-Grumbach M., Nicholson G. A. (2001) Nat. Genet. 27, 309–312 - PubMed
-
- Bejaoui K., Wu C., Scheffler M. D., Haan G., Ashby P., Wu L., de Jong P., Brown R. H., Jr. (2001) Nat. Genet. 27, 261–262 - PubMed
-
- Hanada K., Hara T., Fukasawa M., Yamaji A., Umeda M., Nishijima M. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 33787–33794 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

