Environmental neurotoxic pesticide increases histone acetylation to promote apoptosis in dopaminergic neuronal cells: relevance to epigenetic mechanisms of neurodegeneration
- PMID: 20097775
- PMCID: PMC2847769
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.109.062174
Environmental neurotoxic pesticide increases histone acetylation to promote apoptosis in dopaminergic neuronal cells: relevance to epigenetic mechanisms of neurodegeneration
Abstract
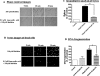
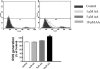
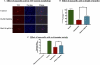
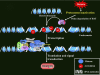
Pesticide exposure has been implicated in the etiopathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD); in particular, the organochlorine insecticide dieldrin is believed to be associated with PD. Emerging evidence indicates that histone modifications play a critical role in cell death. In this study, we examined the effects of dieldrin treatment on histone acetylation and its role in dieldrin-induced apoptotic cell death in dopaminergic neuronal cells. In mesencephalic dopaminergic neuronal cells, dieldrin induced a time-dependent increase in the acetylation of core histones H3 and H4. Histone acetylation occurred within 10 min of dieldrin exposure indicating that acetylation is an early event in dieldrin neurotoxicity. The hyperacetylation was attributed to dieldrin-induced proteasomal dysfunction, resulting in accumulation of a key histone acetyltransferase (HAT), cAMP response element-binding protein. The novel HAT inhibitor anacardic acid significantly attenuated dieldrin-induced histone acetylation, Protein kinase C delta proteolytic activation and DNA fragmentation in dopaminergic cells protected against dopaminergic neuronal degeneration in primary mesencephalic neuronal cultures. Furthermore, 30-day exposure of dieldrin in mouse models induced histone hyperacetylation in the striatum and substantia nigra. For the first time, our results collectively demonstrate that exposure to the neurotoxic pesticide dieldrin induces acetylation of core histones because of proteasomal dysfunction and that hyperacetylation plays a key role in dopaminergic neuronal degeneration after exposure of dieldrin.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Paraquat induces epigenetic changes by promoting histone acetylation in cell culture models of dopaminergic degeneration.Neurotoxicology. 2011 Oct;32(5):586-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2011.05.018. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Neurotoxicology. 2011. PMID: 21777615 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental neurotoxin dieldrin induces apoptosis via caspase-3-dependent proteolytic activation of protein kinase C delta (PKCdelta): Implications for neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease.Mol Brain. 2008 Oct 22;1:12. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-1-12. Mol Brain. 2008. PMID: 18945348 Free PMC article.
-
Dieldrin induces ubiquitin-proteasome dysfunction in alpha-synuclein overexpressing dopaminergic neuronal cells and enhances susceptibility to apoptotic cell death.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Oct;315(1):69-79. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.084632. Epub 2005 Jun 29. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 15987830
-
Dieldrin-induced neurotoxicity: relevance to Parkinson's disease pathogenesis.Neurotoxicology. 2005 Aug;26(4):701-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2004.07.010. Neurotoxicology. 2005. PMID: 16112328 Review.
-
Epigenetic landscape of amphetamine and methamphetamine addiction in rodents.Epigenetics. 2015;10(7):574-80. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1055441. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26023847 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Age-related epigenetic regulation in the brain and its role in neuronal diseases.BMB Rep. 2016 Dec;49(12):671-680. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.12.184. BMB Rep. 2016. PMID: 27866512 Free PMC article.
-
The Synapse as a Central Target for Neurodevelopmental Susceptibility to Pesticides.Toxics. 2016 Aug 26;4(3):18. doi: 10.3390/toxics4030018. Toxics. 2016. PMID: 29051423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EDC-2: The Endocrine Society's Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals.Endocr Rev. 2015 Dec;36(6):E1-E150. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1010. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Endocr Rev. 2015. PMID: 26544531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired Mitophagy and Protein Acetylation Levels in Fibroblasts from Parkinson's Disease Patients.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Apr;56(4):2466-2481. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1206-6. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30032424
-
Environmental chemical exposures and human epigenetics.Int J Epidemiol. 2012 Feb;41(1):79-105. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyr154. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Int J Epidemiol. 2012. PMID: 22253299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afeseh Ngwa H, Kanthasamy A, Anantharam V, Song C, Witte T, Houk R, Kanthasamy AG. (2009) Vanadium induces dopaminergic neurotoxicity via protein kinase Cdelta dependent oxidative signaling mechanisms: relevance to etiopathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 240:273–285 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aron JL, Parthun MR, Marcucci G, Kitada S, Mone AP, Davis ME, Shen T, Murphy T, Wickham J, Kanakry C, et al. (2003) Depsipeptide (FR901228) induces histone acetylation and inhibition of histone deacetylase in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells concurrent with activation of caspase 8-mediated apoptosis and down-regulation of c-FLIP protein. Blood 102:652–658 - PubMed
-
- Bader N, Jung T, Grune T. (2007) The proteasome and its role in nuclear protein maintenance. Exp Gerontol 42:864–870 - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanyam K, Swaminathan V, Ranganathan A, Kundu TK. (2003) Small molecule modulators of histone acetyltransferase p300. J Biol Chem 278:19134–40 - PubMed
-
- Boutillier AL, Trinh E, Loeffler JP. (2003) Selective E2F-dependent gene transcription is controlled by histone deacetylase activity during neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem 84:814–828 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

