Quantitative site-specific phosphorylation dynamics of human protein kinases during mitotic progression
- PMID: 20097925
- PMCID: PMC2877978
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M900335-MCP200
Quantitative site-specific phosphorylation dynamics of human protein kinases during mitotic progression
Abstract
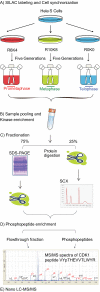
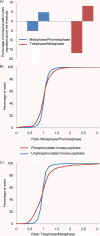
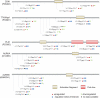
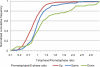
Reversible protein phosphorylation is a key regulatory mechanism of mitotic progression. Importantly, protein kinases themselves are also regulated by phosphorylation-dephosphorylation processes; hence, phosphorylation dynamics of kinases hold a wealth of information about phosphorylation networks. Here, we investigated the site-specific phosphorylation dynamics of human kinases during mitosis using synchronization of HeLa suspension cells, kinase enrichment, and high resolution mass spectrometry. In biological triplicate analyses, we identified 206 protein kinases and more than 900 protein kinase phosphorylation sites, including 61 phosphorylation sites on activation segments, and quantified their relative abundances across three specific mitotic stages. Around 25% of the kinase phosphorylation site ratios were found to be changed by at least 50% during mitotic progression. Further network analysis of jointly regulated kinase groups suggested that Cyclin-dependent kinase- and mitogen-activated kinase-centered interaction networks are coordinately down- and up-regulated in late mitosis, respectively. Importantly, our data cover most of the already known mitotic kinases and, moreover, identify attractive candidates for future studies of phosphorylation-based mitotic signaling. Thus, the results of this study provide a valuable resource for cell biologists and provide insight into the system properties of the mitotic phosphokinome.
Figures



References
-
- Cohen P. (2002) The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat. Cell Biol 4, E127–E130 - PubMed
-
- Pawson T., Scott J. D. (2005) Protein phosphorylation in signaling–50 years and counting. Trends Biochem. Sci 30, 286–290 - PubMed
-
- Graves J. D., Krebs E. G. (1999) Protein phosphorylation and signal transduction. Pharmacol. Ther 82, 111–121 - PubMed
-
- Manning G., Whyte D. B., Martinez R., Hunter T., Sudarsanam S. (2002) The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 298, 1912–1934 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

