Tunable plasmonic nanobubbles for cell theranostics
- PMID: 20097970
- PMCID: PMC3074956
- DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/21/8/085102
Tunable plasmonic nanobubbles for cell theranostics
Erratum in
- Nanotechnology. 2016 Mar 11;27(10):109501
Abstract
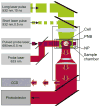
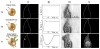
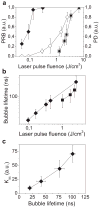
Combining diagnostic and therapeutic processes into one (theranostics) and improving their selectivity to the cellular level may offer significant benefits in various research and disease systems and currently is not supported with efficient methods and agents. We have developed a novel method based on the gold nanoparticle-generated transient photothermal vapor nanobubbles, that we refer to as plasmonic nanobubbles (PNB). After delivery and clusterization of the gold nanoparticles (NP) to the target cells the intracellular PNBs were optically generated and controlled through the laser fluence. The PNB action was tuned in individual living cells from non-invasive high-sensitive imaging at lower fluence to disruption of the cellular membrane at higher fluence. We have achieved non-invasive 50-fold amplification of the optical scattering amplitude with the PNBs (relative to that of NPs), selective mechanical and fast damage to specific cells with bigger PNBs, and optical guidance of the damage through the damage-specific signals of the bubbles. Thus the PNBs acted as tunable theranostic agents at the cellular level and in one process that have supported diagnosis, therapy and guidance of the therapy.
Figures
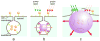
Similar articles
-
Plasmonic nanobubbles as transient vapor nanobubbles generated around plasmonic nanoparticles.ACS Nano. 2010 Apr 27;4(4):2109-23. doi: 10.1021/nn1000222. ACS Nano. 2010. PMID: 20307085 Free PMC article.
-
The in vivo performance of plasmonic nanobubbles as cell theranostic agents in zebrafish hosting prostate cancer xenografts.Biomaterials. 2010 Oct;31(29):7567-74. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.06.031. Epub 2010 Jul 14. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 20630586 Free PMC article.
-
Transient photothermal spectra of plasmonic nanobubbles.Langmuir. 2012 Mar 13;28(10):4858-66. doi: 10.1021/la205132x. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Langmuir. 2012. Retraction in: Langmuir. 2017 Apr 25;33(16):4090. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b01145. PMID: 22339620 Retracted.
-
Plasmonic gold nanoparticles: Optical manipulation, imaging, drug delivery and therapy.J Control Release. 2019 Oct;311-312:170-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.08.032. Epub 2019 Aug 28. J Control Release. 2019. PMID: 31472191 Review.
-
Methods for Generation and Detection of Nonstationary Vapor Nanobubbles Around Plasmonic Nanoparticles.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1530:165-192. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6646-2_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28150203 Review.
Cited by
-
Photothermal nanoblade for patterned cell membrane cutting.Opt Express. 2010 Oct 25;18(22):23153-60. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.023153. Opt Express. 2010. PMID: 21164656 Free PMC article.
-
Remotely Triggered Nano-Theranostics For Cancer Applications.Nanotheranostics. 2017;1(1):1-22. doi: 10.7150/ntno.17109. Nanotheranostics. 2017. PMID: 28191450 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging and drug delivery using theranostic nanoparticles.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Aug 30;62(11):1052-1063. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2010.08.004. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010. PMID: 20709124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rainbow Plasmonic Nanobubbles: Synergistic Activation of Gold Nanoparticle Clusters.J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2011 Jan 1;2(104):1-8. doi: 10.4172/2157-7439.1000104. J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21804947 Free PMC article.
-
Improved cellular specificity of plasmonic nanobubbles versus nanoparticles in heterogeneous cell systems.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34537. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034537. Epub 2012 Apr 3. PLoS One. 2012. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2017 Nov 2;12(11):e0187820. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187820. PMID: 22509318 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
