Isoflurane does not affect brain cell death, hippocampal neurogenesis, or long-term neurocognitive outcome in aged rats
- PMID: 20098132
- PMCID: PMC5214622
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181ca33a1
Isoflurane does not affect brain cell death, hippocampal neurogenesis, or long-term neurocognitive outcome in aged rats
Abstract
Background: Roughly, 10% of elderly patients develop postoperative cognitive dysfunction. General anesthesia impairs spatial memory in aged rats, but the mechanism is not known. Hippocampal neurogenesis affects spatial learning and memory in rats, and isoflurane affects neurogenesis in neonatal and young adult rats. We tested the hypothesis that isoflurane impairs neurogenesis and hippocampal function in aged rats.
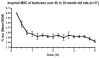
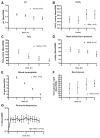
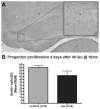
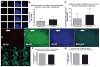
Methods: Isoflurane was administered to 16-month-old rats at one minimum alveolar concentration for 4 h. FluoroJade staining was performed to assess brain cell death 16 h after isoflurane administration. Dentate gyrus progenitor proliferation was assessed by bromodeoxyuridine injection 4 days after anesthesia and quantification of bromodeoxyuridine+ cells 12 h later. Neuronal differentiation was studied by determining colocalization of bromodeoxyuridine with the immature neuronal marker NeuroD 5 days after anesthesia. New neuronal survival was assessed by quantifying cells coexpressing bromodeoxyuridine and the mature neuronal marker NeuN 5 weeks after anesthesia. Four months after anesthesia, associative learning was assessed by fear conditioning. Spatial reference memory acquisition and retention was tested in the Morris Water Maze.
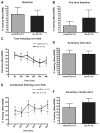
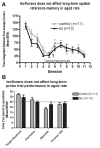
Results: Cell death was sporadic and not different between groups. We did not detect any differences in hippocampal progenitor proliferation, neuronal differentiation, new neuronal survival, or in any of the tests of long-term hippocampal function.
Conclusion: In aged rats, isoflurane does not affect brain cell death, hippocampal neurogenesis, or long-term neurocognitive outcome.
Figures

References
-
- Moller JT, Cluitmans P, Rasmussen LS, Houx P, Rasmussen H, Canet J, Rabbitt P, Jolles J, Larsen K, Hanning CD, Langeron O, Johnson T, Lauven PM, Kristensen PA, Biedler A, van Beem H, Fraidakis O, Silverstein JH, Beneken JE, Gravenstein JS. Long-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly ISPOCD1 study. ISPOCD investigators International Study of Post-Operative Cognitive Dysfunction. Lancet. 1998;351:857–61. - PubMed
-
- Monk TG, Weldon BC, Garvan CW, Dede DE, van der Aa MT, Heilman KM, Gravenstein JS. Predictors of cognitive dysfunction after major noncardiac surgery. Anesthesiology. 2008;108:18–30. - PubMed
-
- Culley DJ, Baxter M, Yukhananov R, Crosby G. The memory effects of general anesthesia persist for weeks in young and aged rats. Anesth Analg. 2003;96:1004–9. - PubMed
-
- Culley DJ, Baxter MG, Crosby CA, Yukhananov R, Crosby G. Impaired acquisition of spatial memory 2 weeks after isoflurane and isoflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia in aged rats. Anesth Analg. 2004;99:1393–7. - PubMed
-
- Culley DJ, Baxter MG, Yukhananov R, Crosby G. Long-term impairment of acquisition of a spatial memory task following isoflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia in rats. Anesthesiology. 2004;100:309–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

