Metabolic surgery: the role of the gastrointestinal tract in diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 20098450
- PMCID: PMC2999518
- DOI: 10.1038/nrendo.2009.268
Metabolic surgery: the role of the gastrointestinal tract in diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Several conventional methods of bariatric surgery can induce long-term remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM); novel gastrointestinal surgical procedures are reported to have similar effects. These procedures also dramatically improve other metabolic conditions, including hyperlipidemia and hypertension, in both obese and nonobese patients. Several studies have provided evidence that these metabolic effects are not simply the results of drastic weight loss and decreased caloric intake but might be attributable, in part, to endocrine changes resulting from surgical manipulation of the gastrointestinal tract. In this Review, we provide an overview of the clinical evidence that demonstrates the effects of such interventions-termed metabolic surgery-on T2DM and discuss the implications for future research. In light of the evidence presented here, we speculate that the gastrointestinal tract might have a role in the pathophysiology of T2DM and obesity.
Figures
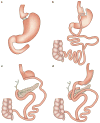
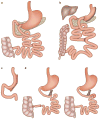
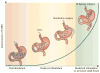
References
-
- Buchwald H, et al. Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292:1724–1737. - PubMed
-
- Cohen R, Pinheiro JS, Correa JL, Schiavon CA. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for BMI < 35 kg/m(2): a tailored approach. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2006;2:401–4. - PubMed
-
- Lee WJ, et al. Effect of laparoscopic mini-gastric bypass for type 2 diabetes mellitus: comparison of BMI>35 and <35 kg/m2. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12:945–52. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien PE, et al. Treatment of mild to moderate obesity with laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding or an intensive medical program: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:625–33. - PubMed
-
- Suter M, Calmes JM, Romy A, Giusti V. Results of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in morbidly obese vs. super obese patients: similar body weight loss, correction of comorbidities, and improvement of quality of life. Arch Surg. 2009;144:312–18. - PubMed

