First year experience with newly developed Leksell Gamma Knife Perfexion
- PMID: 20098561
- PMCID: PMC2807679
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-6203.54848
First year experience with newly developed Leksell Gamma Knife Perfexion
Abstract
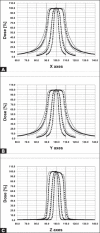
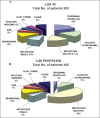
A new model of Leksell Gamma Knife(R) (LGK), known as Perfexion (LGK PFX), was introduced by Elekta Instrument, AB, Sweden, in 2006. This model has a radically different design from the earlier models U, B, C and 4C. Dosimetric characteristics of LGK PFX, technical differences between LGK PFX and LGK 4C, experience gained with acceptance testing and commissioning of the LGK PFX, and comparison between LGK PFX and LGK 4C are presented in this study. Excellent agreement is found between the manufacturers recommended values of absorbed dose rate, relative output factors for 4 and 8 mm collimators, coincidence of mechanical and dosimetric isocenter, FWHM for beam profiles for various collimators and those reported in the present study. Excellent agreement is also found between the dosimetric characteristics of LGK PFX and LGK 4C for the 4 and 8 mm collimators. Examples of clinical cases treated with LGK PFX and impact of LGK PFX on workflow and dosimetric conformity of treatment planning is also given. The set up and treatment of patients on the LGK PFX is much more efficient since it is a fully automated system. The system also provides more options to generate plan with high dosimetric conformity.
Keywords: Leksell Gamma Knife PERFEXION; Leksell Gamma Knife dosimetry; Leksell Gamma Knife treatment planning.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dosimetric characteristics and quality control tests for the collimator sectors of the Leksell Gamma Knife(®) Perfexion(TM).Med Phys. 2012 Jan;39(1):231-6. doi: 10.1118/1.3668057. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22225292
-
Efficiency and dose planning comparisons between the Perfexion and 4C Leksell Gamma Knife units.Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2009;87(3):191-8. doi: 10.1159/000222663. Epub 2009 Jun 3. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2009. PMID: 19494568
-
Evaluation of Clinical Application and Dosimetric Comparison of Treatment Plans of Gamma Knife and CyberKnife in Treating Arteriovenous Malformations.Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2017;95(3):142-148. doi: 10.1159/000460259. Epub 2017 May 10. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 28486221
-
3-D treatment planning system-Leksell Gamma Knife treatment planning system.Med Dosim. 2018 Summer;43(2):177-183. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Med Dosim. 2018. PMID: 29656889 Review.
-
[Radiosurgery of the brain at the beginning of the 21st century: gamma knife with C-table].Orv Hetil. 2001 Oct 7;142(40):2181-92. Orv Hetil. 2001. PMID: 11706510 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Radiosurgery technology development and use.J Radiosurg SBRT. 2011;1(1):21-29. J Radiosurg SBRT. 2011. PMID: 29296294 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetry and Treatment Descriptions Using the First Completely Automated Stereotactic Intracranial Radiosurgery Rotating Gamma Ray Unit in America.Cureus. 2018 Apr 27;10(4):e2542. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2542. Cureus. 2018. PMID: 29963336 Free PMC article.
-
Filmless quality assurance of a Leksell Gamma Knife® Icon™.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2021 Jan;22(1):59-67. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13070. Epub 2020 Dec 10. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33300664 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-specific independent 3D GammaPlan quality assurance for Gamma Knife Perfexion radiosurgery.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2013 Jan 7;14(1):3949. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v14i1.3949. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23318382 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment Planning for Self-Shielded Radiosurgery.Cureus. 2017 Sep 8;9(9):e1663. doi: 10.7759/cureus.1663. Cureus. 2017. PMID: 29152420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leksell L. The stereotaxic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir Scand. 1951;102:316–9. - PubMed
-
- Lunsford LD, Flickinger J, Lindner G, Maitz A. Stereotactic radiosurgery of the brain using the first United States 201 cobalt-60 source gamma knife. Neurosurgery. 1989;24:151–9. - PubMed
-
- Wu A, Lindner G, Maitz AH, Kalend AM, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC, et al. Physics of Gamma Knife approach on convergent beams in stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1990;18:941–9. - PubMed
-
- Phillips MH, editor. Physical Aspects of Stereotactic Radiosurgery. New York: Plenum Publishing Corporation; 1993.
-
- Webb S. Conformal Radiotherapy, Radiosurgery and Treatment Planning. Bristol: IOP Publishing Ltd; 1993. The Physics of Three-dimensional Radiation Therapy.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

