The art of healing broken hearts in breast cancer patients: Trastuzumab and heart failure
- PMID: 20098570
- PMCID: PMC2807779
The art of healing broken hearts in breast cancer patients: Trastuzumab and heart failure
Abstract
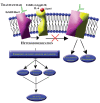
Breast cancer, a leading cause of increased morbidity and mortality among women, overexpresses the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 in approximately 20% to 30% of cases. Trastuzumab (Trz), a monoclonal antibody against the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, improves survival in breast cancer patients in both the adjuvant and metastatic settings. Despite the therapeutic benefits of Trz, there is an increased incidence of cardiotoxicity, particularly when administered following anthracycline-based chemotherapy. The pathogenesis underlying Trz-mediated cardiotoxicity remains poorly understood. The present review focuses on the current understanding of Trz-mediated cardiotoxicity from both the basic and clinical science perspectives.
Keywords: Cardiac MRI; Cardiomyopathy; Echocardiography; Renin-angiotensin system; Trastuzumab.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trastuzumab-induced cardiac dysfunction: A 'dual-hit'.Exp Clin Cardiol. 2011 Fall;16(3):70-4. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 22065936 Free PMC article.
-
Three-year follow-up from a phase 3 study of SB3 (a trastuzumab biosimilar) versus reference trastuzumab in the neoadjuvant setting for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2019 Oct;120:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.07.015. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Eur J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31445454 Clinical Trial.
-
The role of renin angiotensin system antagonists in the prevention of doxorubicin and trastuzumab induced cardiotoxicity.Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2015 Apr 3;13:18. doi: 10.1186/s12947-015-0011-x. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2015. PMID: 25889218 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Benefits of antihypertensive medications for anthracycline- and trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity in patients with breast cancer: Insights from recent clinical trials.Indian J Pharmacol. 2016 Sep-Oct;48(5):490-497. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.190719. Indian J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27721532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catching broken hearts: pre-clinical detection of doxorubicin and trastuzumab mediated cardiac dysfunction in the breast cancer setting.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014 Jul;92(7):546-50. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2013-0470. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24959994 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk factors for anthracycline-associated cardiotoxicity.Support Care Cancer. 2016 May;24(5):2173-2180. doi: 10.1007/s00520-015-3008-y. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Support Care Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26563179 Free PMC article.
-
Trastuzumab-induced cardiac dysfunction: A 'dual-hit'.Exp Clin Cardiol. 2011 Fall;16(3):70-4. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 22065936 Free PMC article.
-
Trastuzumab resumption after extremely severe cardiotoxicity in metastatic breast cancer patient: a case report.BMC Cancer. 2017 Nov 7;17(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3712-8. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29115937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer. 2001;94:153–6. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J. A new anti-ErbB2 strategy in the treatment of cancer: Prevention of ligand-dependent ErbB2 receptor heterodimerization. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:93–5. - PubMed
-
- Lalloo F, Varley J, Ellis D, et al. Early Onset Breast Cancer Study Group Prediction of pathogenic mutations in patients with early-onset breast cancer by family history. Lancet. 2003;361:1101–2. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials