Risk factors of type 2 diabetes among Korean adults: The 2001 Korean national health and nutrition examination survey
- PMID: 20098581
- PMCID: PMC2809235
- DOI: 10.4162/nrp.2009.3.4.286
Risk factors of type 2 diabetes among Korean adults: The 2001 Korean national health and nutrition examination survey
Abstract
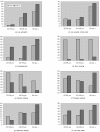
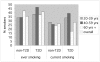
This study aimed to identify risk factors for type 2 diabetes (T2D) in Korea, a rapidly changing country. Data of 5,132 adults aged 20-85 were used from the 2001 Korean Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Multiple logistic regression was carried out to identify risk factors for T2D. Three models were specified: (i) socioeconomic and demographic factors (model 1: age, gender, education, poverty income ratio, employment), (ii) behavioral risk factors and covariates (model 2: obesity, physical activity, smoking, alcohol drinking, dietary quality, family history of T2D, co-morbidity) and (iii) socioeconomic, demographic, and behavioral factors (model 3). The prevalence of T2D was 7.4%. Less education (OR 1.41, 95% CI 1.08-1.84), age (OR 2.19, 95% CI 1.56-3.08 in 40-59 yrs, OR 4.05, 95% CI 2.76-5.95 in 60 yrs + comparing to 20-39 yrs) and abdominal obesity (OR 2.24, 95% CI 1.79-2.82) were risk factors for T2D even after controlling for other factors simultaneously. There was a significant association of T2D with ever smoking (OR 1.34, 95% CI 1.06-1.67). The relationship of age with T2D was modified by gender in model 1 and the relationship of smoking with T2D was modified by obesity in model 2. Less educated, older, obese or ever smokers were more likely to have T2D. Gender mediated the relationship of age, and obesity mediated the relationship of smoking, with T2D. Intervention programs for T2D in Korea should take the interactions among risk factors into account.
Keywords: Korea health and nutrition examination survey 2001; Korean adult; Type 2 diabetes; risk factor.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Delaimy WK, Willett WC, Mansen JE, Speizer FE, Hu FB. Smoking and mortality among women with type 2 diabetes: The nurses's health study cohort. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:2043–2048. - PubMed
-
- Chen GLX, Wang JJ, Xing X, Yang W, Hu Y. Obesity, coronary heart disease risk factors and diabetes in Chenese: an approach to the criteria of obesity in the Chinese population. Obes Rev. 2002;2002:167–172. - PubMed
-
- Cho NH, Jang HC, Park HK, Cho YW. Waist circumference is the key risk factor for diabetes in Korean women with history of gestational diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;71:177–183. - PubMed
-
- Dalstra JAA, Kunst AE, Borrell C, Breeze C, Cambois E, Costa G, Geurts JJ, Lahelma E, Van Oyen H, Rasmussen NK, Regidor E, Spadea T, Mackenbach JP. Socioeconomic differences in the prevalence of common chronic diseases: an overview of eight European countries. Int J Epidemiol. 2005;34:316–326. - PubMed