3-O-methylfunicone, a selective inhibitor of mammalian Y-family DNA polymerases from an Australian sea salt fungal strain
- PMID: 20098603
- PMCID: PMC2810227
- DOI: 10.3390/md7040624
3-O-methylfunicone, a selective inhibitor of mammalian Y-family DNA polymerases from an Australian sea salt fungal strain
Abstract
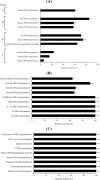
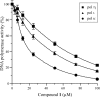
We isolated a pol inhibitor from the cultured mycelia extract of a fungal strain isolated from natural salt from a sea salt pan in Australia, which was identified as 3-O-methylfunicone by spectroscopic analyses. This compound selectively inhibited the activities of mammalian Y-family DNA polymerases (pols) (i.e., pols eta, iota and kappa). Among these pols, human pol kappa activity was most strongly inhibited, with an IC(50) value of 12.5 microM. On the other hand, the compound barely influenced the activities of the other families of mammalian pols, such as A-family (i.e., pol gamma), B-family (i.e., pols alpha, delta and epsilon) or X-family (i.e., pols beta, lambda and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase), and showed no effect on the activities of fish pol delta, plant pols, prokaryotic pols and other DNA metabolic enzymes, such as calf primase of pol alpha, human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase, human telomerase, T7 RNA polymerase, mouse IMP dehydrogenase (type II), human topoisomerases I and II, T4 polynucleotide kinase or bovine deoxyribonuclease I. This compound also suppressed the growth of two cultured human cancer cell lines, HCT116 (colon carcinoma cells) and HeLa (cervix carcinoma cells), and UV-treated HeLa cells exhibited lower clonogenic survival in the presence of inhibitor.
Keywords: 3-O-methylfunicone; Australian sea salt; DNA polymerase κ; Y-family DNA polymerase; anti-cancer drug; enzyme inhibitor; marine fungal strains.
Figures
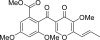



Similar articles
-
Penicilliols A and B, novel inhibitors specific to mammalian Y-family DNA polymerases.Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Mar 1;17(5):1811-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.01.064. Epub 2009 Feb 1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19223184
-
1-deoxyrubralactone, a novel specific inhibitor of families X and Y of eukaryotic DNA polymerases from a fungal strain derived from sea algae.Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Mar 15;16(6):2939-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.12.044. Epub 2007 Dec 25. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18178092
-
β-Sitosteryl (6'-O-linoleoyl)-glucoside of soybean (Glycine max L.) crude extract inhibits Y-family DNA polymerases.J Oleo Sci. 2010;59(11):621-30. doi: 10.5650/jos.59.621. J Oleo Sci. 2010. PMID: 20972363
-
Inhibitory effect on replicative DNA polymerases, human cancer cell proliferation, and in vivo anti-tumor activity by glycolipids from spinach.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(9):955-67. doi: 10.2174/092986707780362952. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17439396 Review.
-
What makes y family pols potential candidates for molecular targeted therapies and novel biotechnological applications.Curr Mol Med. 2014 Jan;14(1):96-114. doi: 10.2174/15665240113136660080. Curr Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24160487 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive strategy to discover inhibitors of the translesion synthesis DNA polymerase κ.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e45032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045032. Epub 2012 Oct 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056190 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Damage Tolerance Pathways in Human Cells: A Potential Therapeutic Target.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 7;11:822500. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.822500. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35198436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the error-prone DNA polymerase Polκ by oncogenic signaling and its contribution to drug resistance.Sci Signal. 2020 Apr 28;13(629):eaau1453. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aau1453. Sci Signal. 2020. PMID: 32345725 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage tolerance: a double-edged sword guarding the genome.Transl Cancer Res. 2013;2(3):107-129. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-676X.2013.04.01. Transl Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24058901 Free PMC article.
-
DNA polymerases and cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2011 Feb;11(2):96-110. doi: 10.1038/nrc2998. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21258395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DePamphilis ML. DNA Replication in Eukaryotic Cells. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; New York, NY, USA: 1996.
-
- Hubscher U, Maga G, Spadari S. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Ann Rev Biochem. 2002;71:133–163. - PubMed
-
- Bebenek K, Kunkel TA. DNA repair and replication. In: Yang W, editor. Advances in Protein Chemistry. Vol. 69. Elsevier; San Diego, CA, USA: 2004. pp. 137–165. - PubMed
-
- Takata K, Shimizu T, Iwai S, Wood RD. Human DNA polymerase N (POLN) is a low fidelity enzyme capable of error-free bypass of 5S-thymine glycol. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:23445–23455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
