Terpenyl-purines from the sea
- PMID: 20098613
- PMCID: PMC2810218
- DOI: 10.3390/md7040833
Terpenyl-purines from the sea
Abstract
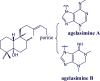
Agelasines, asmarines and related compounds are natural products with a hybrid terpene-purine structure isolated from numerous genera of sponges (Agela sp., Raspailia sp.). Some agelasine analogs and related structures have displayed high general toxicity towards protozoa, and have exhibited broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against a variety of species, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and also an important cytotoxic activity against several cancer cell lines, including multidrug-resistant ones. Of particular interest in this context are the asmarines (tetrahydro[1,4]diazepino[1,2,3-g,h]purines), which have shown potent antiproliferative activity against several types of human cancer cell lines. This review summarizes the sources of isolation, chemistry and bioactivity of marine alkylpurines and their bioactive derivatives.
Keywords: agelasimine; agelasine; ageline; alkyl-purine; asmarine; terpene-purine; terpenylpurine.
Figures
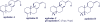
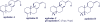
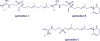
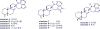

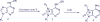
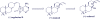
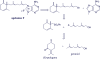
References
-
- Li M-Y, Xiao O, Pan JY, Wu J. Natural products from semi-mangrove flora: Source, chemistry and bioactivities. Nat Prod Rep. 2009;26:281–298. - PubMed
-
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM, Kingston DGI. Natural products as pharmaceuticals and sources for lead structures. In: Wermuth CG, editor. The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry. 3rd ed. Academic Press; London, UK: 2003. pp. 159–186.
-
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007;70:461–477. - PubMed
-
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM, Snader KM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J. Nat. Prod. 2003;66:1022–1037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
