SPECT Imaging of Teboroxime during Myocardial Blood Flow Changes
- PMID: 20098635
- PMCID: PMC2809426
- DOI: 10.1109/23.856535
SPECT Imaging of Teboroxime during Myocardial Blood Flow Changes
Abstract
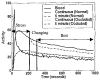
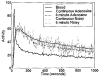
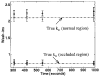
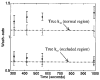
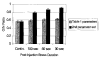
Kinetic parameters and static images from dynamic SPECT imaging of (99m)Tc-teboroxime have been shown to reflect blood flow in dogs and in humans at rest and during adenosine stress. When compartment modeling is used, steady-state physiological conditions are assumed. With standard adenosine stress protocols, imaging of teboroxime would likely involve significant changes in flow, even if performed only for five minutes. These flow changes may significantly bias the kinetic parameter estimates. On the other hand, when static imaging is performed, large flow changes during acquisition may improve contrast between normal and occluded regions. Computer simulations were performed to determine the effect of changing flows on kinetic parameter estimation and on static (average tissue uptake) images. Two canine studies were also performed in which adenosine was given with a standard protocol, and then imaging was repeated with adenosine infusion held constant. The simulations predicted biases on the order of 7% for kinetic washin parameter estimation and 18% for the washout parameter. Contrast for static studies was found to depend critically on the time-activity behavior of the distribution as well as on the stress protocol. The differences in washin contrast from the standard and continous adenosine dog studies was slightly larger than predicted from the simulations. Optimal imaging of teboroxime with adenosine using compartment modeling will require non-standard adenosine stress protocols, although sub-optimal imaging may still be useful clinically.
Figures
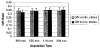
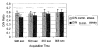
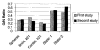
Similar articles
-
Static Versus Dynamic Teboroxime Myocardial Perfusion SPECT in Canines.IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2000 Jun 1;47(3):1112-1117. doi: 10.1109/23.856556. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2000. PMID: 20090867 Free PMC article.
-
Compartmental modeling of technetium-99m-labeled teboroxime with dynamic single-photon emission computed tomography: comparison with static thallium-201 in a canine model.Invest Radiol. 2001 Mar;36(3):178-85. doi: 10.1097/00004424-200103000-00007. Invest Radiol. 2001. PMID: 11228582 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid back to back adenosine stress/rest technetium-99m teboroxime myocardial perfusion SPECT using a triple-detector camera.J Nucl Med. 1993 Sep;34(9):1485-93. J Nucl Med. 1993. PMID: 8355068
-
Clinical experience with technetium 99m teboroxime.Semin Nucl Med. 1991 Jul;21(3):182-9. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2998(05)80039-x. Semin Nucl Med. 1991. PMID: 1948111 Review.
-
Clinical experience with technetium-99m teboroxime, a neutral, lipophilic myocardial perfusion imaging agent.Am J Cardiol. 1990 Oct 16;66(13):63E-67E. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(90)90614-7. Am J Cardiol. 1990. PMID: 2220625 Review.
Cited by
-
Static Versus Dynamic Teboroxime Myocardial Perfusion SPECT in Canines.IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2000 Jun 1;47(3):1112-1117. doi: 10.1109/23.856556. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2000. PMID: 20090867 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Myocardial Perfusion Reserve Using Dynamic SPECT Imaging in Humans: A Feasibility Study.J Nucl Med. 2013 Jun;54(6):873-9. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.109652. Epub 2013 Apr 11. J Nucl Med. 2013. PMID: 23578996 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Simultaneous assessment of cardiac perfusion and function using 5-dimensional imaging with Tc-99m teboroxime.J Nucl Cardiol. 2006 May-Jun;13(3):354-61. doi: 10.1016/j.nuclcard.2006.03.004. J Nucl Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 16750780
References
-
- Stewart RE, Schwaiger M, Hutchins GD, Chiao PC, Gallgher KP, Nguyen N, Petry NA, Rogers WL. Myocardial clearance kinetics of technetium-99m-sq30217: a marker of regional myocardial blood flow. J Nucl Med. 1990;31:1183–11990. - PubMed
-
- Wilson RF, Wyche K, Christensen BV, Zimmer S, Laxson DD. Effects of adenosine on human coronary arterial circulation. Circ. 1990;82:1595–1606. - PubMed
-
- Iskandrian AE. State of the art for pharmacologic stress imaging. In: Zaret, Beller, editors. Nuclear Cardiology. 2. St. Louis: Mosby; 1999. pp. 312–330.
-
- Glover DK, Ruiz M, Bergmann EE, Simanis JP, Smith WH, Watson DD, Beller GA. Myocardial technetium-99m-teboroxime uptake during adenosine-induced hyperemia in dogs with either a critical or mild coronary stenosis: comparison to thallium-201 and regional blood flow. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:476–483. - PubMed
-
- Beanlands R, Muzik O, Nguyen N, Petry N, Schwaiger M. The relationship between myocardial retention of technetium-99m teboroxime and myocardial blood flow. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992;20:712–719. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
