Expanding the substantial interactome of NEMO using protein microarrays
- PMID: 20098747
- PMCID: PMC2808332
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008799
Expanding the substantial interactome of NEMO using protein microarrays
Abstract
Signal transduction by the NF-kappaB pathway is a key regulator of a host of cellular responses to extracellular and intracellular messages. The NEMO adaptor protein lies at the top of this pathway and serves as a molecular conduit, connecting signals transmitted from upstream sensors to the downstream NF-kappaB transcription factor and subsequent gene activation. The position of NEMO within this pathway makes it an attractive target from which to search for new proteins that link NF-kappaB signaling to additional pathways and upstream effectors. In this work, we have used protein microarrays to identify novel NEMO interactors. A total of 112 protein interactors were identified, with the most statistically significant hit being the canonical NEMO interactor IKKbeta, with IKKalpha also being identified. Of the novel interactors, more than 30% were kinases, while at least 25% were involved in signal transduction. Binding of NEMO to several interactors, including CALB1, CDK2, SAG, SENP2 and SYT1, was confirmed using GST pulldown assays and coimmunoprecipitation, validating the initial screening approach. Overexpression of CALB1, CDK2 and SAG was found to stimulate transcriptional activation by NF-kappaB, while SYT1 overexpression repressed TNFalpha-dependent NF-kappaB transcriptional activation in human embryonic kidney cells. Corresponding with this finding, RNA silencing of CDK2, SAG and SENP2 reduced NF-kappaB transcriptional activation, supporting a positive role for these proteins in the NF-kappaB pathway. The identification of a host of new NEMO interactors opens up new research opportunities to improve understanding of this essential cell signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
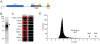

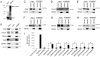
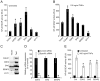
Similar articles
-
NEMO-binding domains of both IKKalpha and IKKbeta regulate IkappaB kinase complex assembly and classical NF-kappaB activation.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 2;284(40):27596-608. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.047563. Epub 2009 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19666475 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Kinase-Mediated Decision Between the Life and Death.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1275:1-33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49844-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33539010
-
Novel non-peptide small molecules preventing IKKβ/NEMO association inhibit NF-κB activation in LPS-stimulated J774 macrophages.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Mar 15;104:83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.01.008. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26776306
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
EDA-ID and IP, two faces of the same coin: how the same IKBKG/NEMO mutation affecting the NF-κB pathway can cause immunodeficiency and/or inflammation.Int Rev Immunol. 2015;34(6):445-59. doi: 10.3109/08830185.2015.1055331. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Int Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26269396 Review.
Cited by
-
Human genome-wide RNAi screen identifies an essential role for inositol pyrophosphates in Type-I interferon response.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Feb 27;10(2):e1003981. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003981. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24586175 Free PMC article.
-
NEMO binds ubiquitinated TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) to regulate innate immune responses to RNA viruses.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e43756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043756. Epub 2012 Sep 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028469 Free PMC article.
-
Polyubiquitin Drives the Molecular Interactions of the NF-κB Essential Modulator (NEMO) by Allosteric Regulation.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 29;290(22):14130-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.640417. Epub 2015 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25866210 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of histamine releasing factor (HRF) as a therapeutic target for treating asthma and allergy.J Asthma Allergy. 2012;5:51-9. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S28868. Epub 2012 Sep 17. J Asthma Allergy. 2012. PMID: 23055753 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB induction of the SUMO protease SENP2: A negative feedback loop to attenuate cell survival response to genotoxic stress.Mol Cell. 2011 Jul 22;43(2):180-91. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.06.017. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21777808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skaug B, Jiang X, Chen ZJ. The role of ubiquitin in NF-kappaB regulatory pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:769–796. - PubMed
-
- Sen R, Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986;46:705–716. - PubMed
-
- Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M. Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:693–733. - PubMed
-
- Yamaoka S, Courtois G, Bessia C, Whiteside ST, Weil R, et al. Complementation cloning of NEMO, a component of the IkappaB kinase complex essential for NF-kappaB activation. Cell. 1998;93:1231–1240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

