Improved SNR in phase contrast velocimetry with five-point balanced flow encoding
- PMID: 20099326
- PMCID: PMC3418793
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22202
Improved SNR in phase contrast velocimetry with five-point balanced flow encoding
Abstract
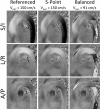
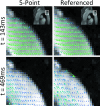
Phase contrast velocimetry can be utilized to measure complex flow for both quantitative and qualitative assessment of vascular hemodynamics. However, phase contrast requires that a maximum measurable velocity be set that balances noise and phase aliasing. To efficiently reduce noise in phase contrast images, several investigators have proposed extended velocity encoding schemes that use extra encodings to unwrap phase aliasing; however, existing techniques can lead to significant increases in echo and scan time, limiting their clinical benefits. In this work, we have developed a novel five-point velocity encoding scheme that efficiently reduces noise with minimal increases in scan and echo time. Investigations were performed in phantoms, demonstrating a 63% increase in velocity-to-noise ratio compared to standard four-point encoding schemes. Aortic velocity measurements were performed in healthy volunteers, showing similar velocity-to-noise ratio improvements. In those volunteers, it was also demonstrated that, without sacrificing accuracy, low-resolution images can be used for the fifth encoding point, reducing the scan time penalty from 25% down to less than 1%.
Figures

Similar articles
-
4D phase contrast MRI at 3 T: effect of standard and blood-pool contrast agents on SNR, PC-MRA, and blood flow visualization.Magn Reson Med. 2010 Feb;63(2):330-8. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22199. Magn Reson Med. 2010. PMID: 20024953
-
Mapping mean and fluctuating velocities by Bayesian multipoint MR velocity encoding-validation against 3D particle tracking velocimetry.Magn Reson Med. 2014 Apr;71(4):1405-15. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24785. Epub 2013 May 13. Magn Reson Med. 2014. PMID: 23670993
-
Peak velocity measurements in tortuous arteries with phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging: the effect of multidirectional velocity encoding.Invest Radiol. 2014 Apr;49(4):189-94. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000013. Invest Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24300842
-
Real-time flow MRI of the aorta at a resolution of 40 msec.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014 Jul;40(1):206-13. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24328. Epub 2013 Oct 11. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24123295
-
Variable velocity encoding in a three-dimensional, three-directional phase contrast sequence: Evaluation in phantom and volunteers.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012 Dec;36(6):1450-9. doi: 10.1002/jmri.23778. Epub 2012 Oct 12. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012. PMID: 23065951
Cited by
-
Deep learning-based velocity antialiasing of 4D-flow MRI.Magn Reson Med. 2022 Jul;88(1):449-463. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29205. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Magn Reson Med. 2022. PMID: 35381116 Free PMC article.
-
Measurements of wall shear stress and aortic pulse wave velocity in swine with familial hypercholesterolemia.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 May;41(5):1475-85. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24681. Epub 2014 Jun 25. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015. PMID: 24964097 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous coherent-incoherent motion imaging in brain parenchyma.Interface Focus. 2025 Apr 4;15(1):20240041. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2024.0041. eCollection 2025 Apr 4. Interface Focus. 2025. PMID: 40191020
-
Repeatability and internal consistency of abdominal 2D and 4D phase contrast MR flow measurements.Acad Radiol. 2013 Jun;20(6):699-704. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2012.12.019. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Acad Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23510798 Free PMC article.
-
Aortic pulse wave velocity measurements with undersampled 4D flow-sensitive MRI: comparison with 2D and algorithm determination.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013 Apr;37(4):853-9. doi: 10.1002/jmri.23877. Epub 2012 Nov 2. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23124585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Markl M, Harloff A, Bley TA, Zaitsev M, Jung B, Weigang E, Langer M, Hennig J, Frydrychowicz A. Time-resolved 3D MR velocity mapping at 3T: improved navigator-gated assessment of vascular anatomy and blood flow. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;25(4):824–831. - PubMed
-
- Kvitting JP, Ebbers T, Wigstrom L, Engvall J, Olin CL, Bolger AF. Flow patterns in the aortic root and the aorta studied with time-resolved, 3-dimensional, phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging: implications for aortic valve-sparing surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;127(6):1602–1607. - PubMed
-
- Wigstrom L, Ebbers T, Fyrenius A, Karlsson M, Engvall J, Wranne B, Bolger AF. Particle trace visualization of intracardiac flow using time-resolved 3D phase contrast MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1999;41(4):793–799. - PubMed
-
- Stalder AF, Russe MF, Frydrychowicz A, Bock J, Hennig J, Markl M. Quantitative 2D and 3D phase contrast MRI: Optimized analysis of blood flow and vessel wall parameters. Magn Reson Med. 2008;60(5):1218–1231. - PubMed
-
- Wu SP, Ringgaard S, Pedersen EM. Three-dimensional phase contrast velocity mapping acquisition improves wall shear stress estimation in vivo. Magn Reson Imaging. 2004;22(3):345–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

