Decreased incidence of NSF in patients on dialysis after changing gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI protocols
- PMID: 20099361
- PMCID: PMC3698801
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.22024
Decreased incidence of NSF in patients on dialysis after changing gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI protocols
Abstract
Purpose: To retrospectively determine the incidence of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) in patients on dialysis administered either a lower dose high-relaxivity linear gadolinium-chelate, gadobenate dimeglumine (MultiHance, MH), compared to a standard dose linear gadolinium chelate, gadodiamide (Omniscan, OM).
Materials and methods: This study was Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)-compliant and Institutional Review Board (IRB)-approved. As per institution standardized contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) protocols, patients on dialysis were imaged using either MH, between 2/2007 to 9/2008, or OM between 10/2003 and 1/2007. Rates of NSF were compared using 95% score-based confidence intervals (CI). The Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to test similarity/difference between contrast doses given to each patient group.
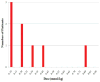
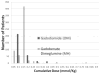
Results: Overall, 312 patients on dialysis received OM and eight (2.6%) developed NSF (95% CI: 1.30%-4.98%). In all, 784 patients on dialysis received MH at a mean cumulative dose of 0.11 mmol/kg (0.05-0.75 mmol/kg) and no cases of NSF were identified (upper 95% confidence bound of 0.45%). The mean cumulative dose of OM was 0.16 mmol/kg (0.1-0.9 mmol/kg) for all patients and 0.28 mmol/kg (0.1-0.8 mmol/kg) for the patients with NSF. The median OM dose was greater in patients who developed NSF (P = 0.03), and was greater than the median MH dose (P < 0.005).
Conclusion: NSF incidence in at-risk patients receiving contrast-enhanced MRI can be reduced after changing contrast administration protocols that includes changing the type and dose of contrast agent.
Figures

References
-
- Cowper SE, Robin HS, Steinberg SM, Su LD, Gupta S, LeBoit PE. Scleromyxedema-like cutaneous disease in renal-dialysis patients. Lancet. 2000;356:1000–1001. - PubMed
-
- Cowper SE, Su LD, Bhawan J, Robin HS, LeBoit PE. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Cowper SE. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy: the first 6 years. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;15:785–790. - PubMed
-
- Kuo PH, Kanal E, Alfa-Abu AK, Cowper SE. Gadolinium-based MR contrast agents and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Radiology. 2007;242:647–649. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

