Enzymatic processing of platinated RNAs
- PMID: 20099814
- PMCID: PMC3230263
- DOI: 10.1021/ja908419j
Enzymatic processing of platinated RNAs
Abstract
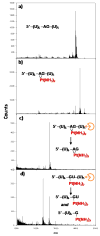
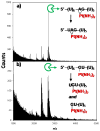
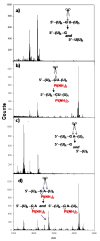
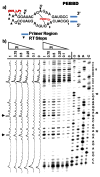
The broadly prescribed antitumor drug cisplatin coordinates to DNA, altering the activity of cellular proteins whose functions rely upon sensing DNA structure. Cisplatin is also known to coordinate to RNA, but the effects of RNA-Pt adducts on the large number of proteins that process the transcriptome are currently unknown. In an effort to address how platination of an RNA alters the function of RNA processing enzymes, we have determined the influence of [Pt(NH(3))(2)](2+)-RNA adducts on the activities of 3'-->5' and 5'-->3' phosphodiesterases, a purine-specific endoribonuclease, and a reverse transcriptase. Single Pt(II) adducts on RNA oligonucleotides of the form (5'-U(6)-XY-U(5)-3': XY = GG, GA, AG, GU) are found to block exonucleolytic digestion. Similar disruption of endonucleolytic cleavage is observed, except for the platinated XY = GA RNA where RNase U2 uniquely tolerates platinum modification. Platinum adducts formed with a more complex RNA prevent reverse transcription, providing evidence that platination is capable of interfering with RNA's role in relaying sequence information. The observed disruptions in enzymatic activity point to the possibility that cellular RNA processing may be similarly affected, which could contribute to the cell-wide effects of platinum antitumor drugs. Additionally, we show that thiourea reverses cisplatin-RNA adducts, providing a chemical tool for use in future studies regarding cisplatin targeting of cellular RNAs.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

