AFM investigations of phase separation in supported membranes of binary mixtures of POPC and an eicosanyl-based bisphosphocholine bolalipid
- PMID: 20099816
- PMCID: PMC2876224
- DOI: 10.1021/la904532s
AFM investigations of phase separation in supported membranes of binary mixtures of POPC and an eicosanyl-based bisphosphocholine bolalipid
Abstract
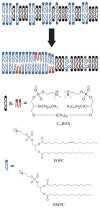
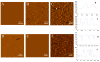
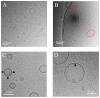
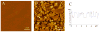
Supported membranes prepared from binary mixtures of DOPC and the bolalipid C(20)BAS have been examined by atomic force microscopy (AFM). The supported membranes are phase separated to give a thicker DOPC-rich phase and a thinner bolalipid-rich phase for a range of lipid compositions. These results confirm an earlier prediction from mean field theory that phase separation is the thermodynamically stable state for membranes containing approximately equimolar C(20)BAS and double chain monopolar lipids with chain lengths exceeding 15 carbons. Hydrophobic mismatch between the monopolar lipid hydrocarbon chains and the membrane spanning bolalipid chains was suggested to provide the driving force for phase separation. The AFM results also show that the morphology of the mixed POPC:C(20)BAS supported membranes varies significantly with the conditions used to prepare the vesicles and supported membrane samples. The complex membrane morphologies observed are attributed to the interplay of several factors, including a compositionally heterogeneous vesicle population, exchange of lipid between the vesicle solution and solid substrate during formation of the supported membrane, and slow equilibration of domains due to pinning of the lipids to the solid support.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phase separation in binary mixtures of bipolar and monopolar lipid dispersions revealed by 2H NMR spectroscopy, small angle x-ray scattering, and molecular theory.Biophys J. 2009 Nov 18;97(10):2700-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.06.058. Biophys J. 2009. PMID: 19917223 Free PMC article.
-
Stability and phase separation in mixed monopolar lipid/bolalipid layers.Biophys J. 2007 Oct 15;93(8):2609-21. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.102764. Epub 2007 Jun 15. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17573422 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-ten-nanometer heterogeneity of solid supported lipid membranes determined by solution atomic force microscopy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Feb;1858(2):181-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26551323
-
AFM for structure and dynamics of biomembranes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jan;1788(1):254-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.08.021. Epub 2008 Sep 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 18822269 Review.
-
Lipid domains in supported lipid bilayer for atomic force microscopy.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;400:503-13. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-519-0_34. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17951756 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Transmembrane Proteins for Phase Separation and Domain Registration in Asymmetric Lipid Bilayers.Biomolecules. 2019 Jul 25;9(8):303. doi: 10.3390/biom9080303. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31349669 Free PMC article.
-
Photouncaging of ceramides promotes reorganization of liquid-ordered domains in supported lipid bilayers.Langmuir. 2013 Mar 12;29(10):3380-7. doi: 10.1021/la3039158. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Langmuir. 2013. PMID: 23402522 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicular and Planar Membranes of Archaea Lipids: Unusual Physical Properties and Biomedical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 9;23(14):7616. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147616. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35886964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase Composition Control in Microsphere-Supported Biomembrane Systems.Langmuir. 2017 Mar 28;33(12):3028-3039. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b04150. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Langmuir. 2017. PMID: 28198634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koga Y, Morii H. Biosci Biotech Biochem. 2005;69:2019. - PubMed
-
- Gambacorta A, Trincone A, Nicolaus B, Lama L, DeRosa M. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1994;16:518.
-
- Gliozzi A, Relini A, Chong PLG. J Memb Sci. 2002;206:131.
-
- Cuccia LA, Morin F, Beck A, Hebert N, Just G, Lennox RB. Chem Eur J. 2000;6:4379–4384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

