Designed semisynthetic protein inhibitors of Ub/Ubl E1 activating enzymes
- PMID: 20099854
- PMCID: PMC2830896
- DOI: 10.1021/ja9088549
Designed semisynthetic protein inhibitors of Ub/Ubl E1 activating enzymes
Abstract
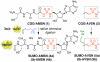
Semisynthetic, mechanism-based protein inhibitors of ubiquitin (Ub) and ubiquitin-like modifier (Ubl) activating enzymes (E1s) have been developed to target E1-catalyzed adenylation and thioesterification of the Ub/Ubl C-terminus during the processes of protein SUMOylation and ubiquitination. The inhibitors were generated by intein-mediated expressed protein ligation using a truncated Ub/Ubl protein (SUMO residues 1-94; Ub residues 1-71) with a C-terminal thioester and synthetic tripeptides having a C-terminal adenosine analogue and an N-terminal cysteine residue. SUMO-AMSN (4a) and Ub-AMSN (4b) contain a sulfamide group as a nonhydrolyzable mimic of the phosphate group in the cognate Ub/Ubl-AMP adenylate intermediate in the first half-reaction, and these constructs selectively inhibit SUMO E1 and Ub E1, respectively, in a dose-dependent manner. SUMO-AVSN (5a) and Ub-AVSN (5b) contain an electrophilic vinyl sulfonamide designed to trap the incoming E1 cysteine nucleophile (Uba2 Cys173 in SUMO E1; Uba1 Cys593 in Ub E1) in the second half-reaction, and these constructs selectively, covalently, and stably cross-link to SUMO E1 and Ub E1, respectively, in a cysteine nucleophile-dependent manner. These inhibitors are powerful tools to probe outstanding mechanistic questions in E1 function and can also be used to study the biological functions of E1 enzymes.
Figures


References
-
-
The human SUMO-1 isoform, human Sae1·Uba2, S. pombe ubiquitin, and S. pombe Uba1 were used for all experiments herein, and are referred to as SUMO, SUMO E1, Ub, and Ub E1, respectively, for simplicity.
-
-
-
(a) SUMO E1:Lois LM, Lima CD. EMBO J. 2005;24:439–451.(b) Nedd8 E1:Walden H, Podgorski MS, Huang DT, Miller DW, Howard RJ, Minor DL, Jr., Holton JM, Schulman BA. Mol. Cell. 2003;12:1427–1437.(c) Ubiquitin E1:Lee I, Schindelin H. Cell. 2008;134:268–278.
-
-
-
Reviewed in:Capili AD, Lima CD. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2007;17:726–735.Dye BT, Schulman BA. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2007;36:131–150.
-
-
-
The sole exception in the E1 family is MoeB, a bacterial biosynthetic enzyme consisting of only the adenylation domain of the corresponding eukaryotic enzymes, which has its cognate MoaD-AMP intermediate bound in its active site:Lake MW, Weubbens MM, Rajagopalan KV, Schindelin H. Nature. 2001;414:325–329.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

