Structure determination and characterization of the vitamin B6 degradative enzyme (E)-2-(acetamidomethylene)succinate hydrolase
- PMID: 20099871
- PMCID: PMC2849673
- DOI: 10.1021/bi901812p
Structure determination and characterization of the vitamin B6 degradative enzyme (E)-2-(acetamidomethylene)succinate hydrolase
Abstract
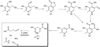
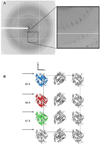
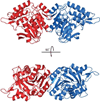
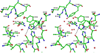
The gene identification and kinetic characterization of (E)-2-(acetamidomethylene)succinate (E-2AMS) hydrolase has recently been described. This enzyme catalyzes the final reaction in the degradation of vitamin B(6) and produces succinic semialdehyde, acetate, ammonia, and carbon dioxide from E-2AMS. The structure of E-2AMS hydrolase was determined to 2.3 A using SAD phasing. E-2AMS hydrolase is a member of the alpha/beta hydrolase superfamily and utilizes a serine/histidine/aspartic acid catalytic triad. Mutation of either the nucleophilic serine or the aspartate resulted in inactive enzyme. Mutation of an additional serine residue in the active site causes the enzyme to be unstable and is likely structurally important. The structure also provides insight into the mechanism of hydrolysis of E-2AMS and identifies several potential catalytically important residues.
Figures




References
-
- Eliot AC, Kirsch JF. Pyridoxal phosphate enzymes: mechanistic, structural, and evolutionary considerations. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004;73:383–415. - PubMed
-
- Snell EE, Haskell BE. The Metabolism of Vitamin B6, In: Comprehensive Biochemistry. Vol. 21. New York: Elsevier/North Holland; 1971.
-
- Kaneko T, Nakamura Y, Sato S, Asamizu E, Kato T, Sasamoto S, Watanabe A, Idesawa K, Ishikawa A, Kawashima K, Kimura T, Kishida Y, Kiyokawa C, Kohara M, Matsumoto M, Matsuno A, Mochizuki Y, Nakayama S, Nakazaki N, Shimpo S, Sugimoto M, Takeuchi C, Yamada M, Tabata S. Complete genome structure of the nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Mesorhizobium loti. DNA Res. 2000;7:331–338. - PubMed
-
- Yuan B, Yoshikane Y, Yokochi N, Ohnishi K, Yagi T. The nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Mesorhizobium loti has and expresses the gene encoding pyridoxine 4-oxidase involved in the degradation of vitamin B6. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004;234:225–230. - PubMed
-
- Funami J, Yoshikane Y, Kobayashi H, Yokochi N, Yuan B, Iwasaki K, Ohnishi K, Yagi T. 4-Pyridoxolactonase from a symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacterium Mesorhizobium loti: cloning, expression, and characterization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2005;1753:234–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

