Mutation versus repair: NEIL1 removal of hydantoin lesions in single-stranded, bulge, bubble, and duplex DNA contexts
- PMID: 20099873
- PMCID: PMC2872175
- DOI: 10.1021/bi901852q
Mutation versus repair: NEIL1 removal of hydantoin lesions in single-stranded, bulge, bubble, and duplex DNA contexts
Abstract
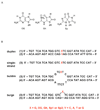
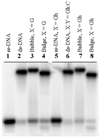
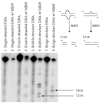
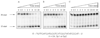
Human DNA glycosylase NEIL1 exhibits a superior ability to remove oxidized guanine lesions guanidinohydantoin (Gh) and spiroiminodihydantoin (Sp) from duplex DNA in comparison to other substrates. In this work, Gh and Sp lesions in bubble, bulge, and single-stranded DNA were found to be good substrates for NEIL1 but were typically excised at much slower rates than from canonical duplex substrates. A notable exception was the activity of NEIL1 on removal of Gh in bubble structures which approaches that of the normal duplex substrate. The cleavage of Gh in the template strand of a replication or transcription bubble may prevent mutations associated with Gh during replication or transcription. However, removal of hydantoin lesions in the absence of an opposite base may also result in strand breaks and potentially deletion and frameshift mutations. Consistent with this as a potential mechanism leading to an N-1 frameshift mutation, the nick left after the removal of the Gh lesion in a DNA bulge by NEIL1 was efficiently religated in the presence of polynucleotide kinase (PNK) and human DNA ligase III (Lig III). These results indicate that NEIL1 does not require a base opposite to identify and remove hydantoin lesions. Depending on the context, the glycosylase activity of NEIL1 may stall replication and prevent mutations or lead to inappropriate removal that may contribute to the mutational spectrum of these unusual lesions.
Figures
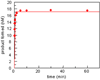
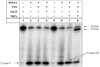
Similar articles
-
Recognition of the oxidized lesions spiroiminodihydantoin and guanidinohydantoin in DNA by the mammalian base excision repair glycosylases NEIL1 and NEIL2.DNA Repair (Amst). 2005 Jan 2;4(1):41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.07.006. DNA Repair (Amst). 2005. PMID: 15533836
-
Superior removal of hydantoin lesions relative to other oxidized bases by the human DNA glycosylase hNEIL1.Biochemistry. 2008 Jul 8;47(27):7137-46. doi: 10.1021/bi800160s. Epub 2008 Jun 11. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18543945 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual structural features of hydantoin lesions translate into efficient recognition by Escherichia coli Fpg.Biochemistry. 2007 Aug 21;46(33):9355-65. doi: 10.1021/bi602459v. Epub 2007 Jul 27. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17655276 Free PMC article.
-
New paradigms in the repair of oxidative damage in human genome: mechanisms ensuring repair of mutagenic base lesions during replication and involvement of accessory proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 May;72(9):1679-98. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1820-z. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25575562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formation and processing of DNA damage substrates for the hNEIL enzymes.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Jun;107:35-52. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.030. Epub 2016 Nov 20. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 27880870 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Low-Activity Polymorphic Variant of Human NEIL2 DNA Glycosylase.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 17;23(4):2212. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042212. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216329 Free PMC article.
-
Substitution of Ala for Tyr567 in RB69 DNA polymerase allows dAMP and dGMP to be inserted opposite Guanidinohydantoin.Biochemistry. 2010 Oct 5;49(39):8554-63. doi: 10.1021/bi100913v. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20795733 Free PMC article.
-
Repair of hydantoin lesions and their amine adducts in DNA by base and nucleotide excision repair.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Sep 18;135(37):13851-61. doi: 10.1021/ja4059469. Epub 2013 Sep 5. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23930966 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Editing of the Human DNA Glycosylase NEIL1 Alters Its Removal of 5-Hydroxyuracil Lesions in DNA.Biochemistry. 2021 May 18;60(19):1485-1497. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00062. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Biochemistry. 2021. PMID: 33929180 Free PMC article.
-
New insights in the removal of the hydantoins, oxidation product of pyrimidines, via the base excision and nucleotide incision repair pathways.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021039. Epub 2011 Jul 25. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21799731 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

